Every four years, the Bitcoin community celebrates the Bitcoin halving.
Many BTC market analysts view this as a quadrennial milestone event due to its historically bullish impact on the cryptocurrency market as a whole.
A key component of Bitcoin’s design is its periodic halving, which ensures the cryptocurrency’s scarcity and acts as a buffer against inflationary pressures.
Bitcoin halvings, which are programmed into Bitcoin’s code, occur about every four years. The block reward is halved with each halving event, and the supply of new Bitcoin (BTC) is directly impacted.
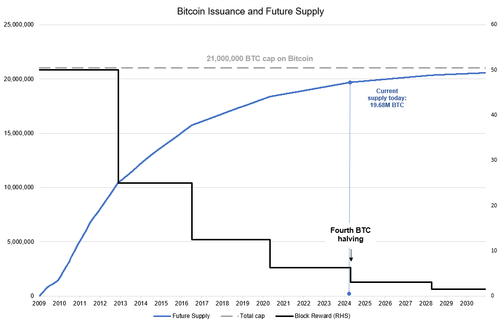
Additionally, halvings add to the intrinsic scarcity of Bitcoin by steadily lowering the rate at which new BTC enters the market. Its predictable and limited supply, which is capped at 21 million coins, supports Bitcoin’s long-term value proposition.
Halvings also reduce inflation by gradually decreasing the supply of new Bitcoin. This predictable inflation control mechanism makes Bitcoin a desirable alternative to conventional fiat currencies, which are vulnerable to unpredictable inflation.
As the market edges closer to Bitcoin's fourth halving within hours, CoinTelegraph's Yashu Gola dives into five fascinating facts about this phenomenon that even seasoned crypto-enthusiasts might not know.
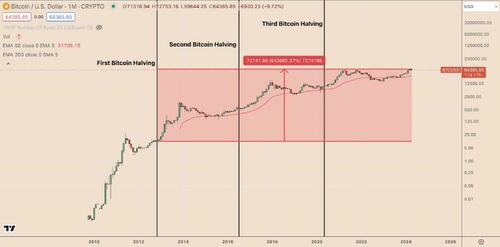
Bitcoin price's up over 650,000% since the first halving
Historically, Bitcoin’s price has increased following a halving, though this largely hinges on the balance of supply and demand.
Historical data provides some insights: After Nov. 28, 2012, the day of Bitcoin’s first halving, its price climbed from $11 to the then-record high of $1,240 a year later. Similarly, after the second halving in July 2016, Bitcoin’s price surged from around $650 to a new record high of $20,000 in December 2017.
In May 2020, after the third halving, Bitcoin's price boomed from around $8,8000 toward $69,000 in November 2021. So, Bitcoin's returns since the first halving stand at an astounding 650,000%.
Multiple catalysts have spurred demand for Bitcoin following its halving events. For instance, during 2020-2021, a generally dovish stance by global central banks significantly contributed to Bitcoin's price rally.
Halvings test miners' economic resilience
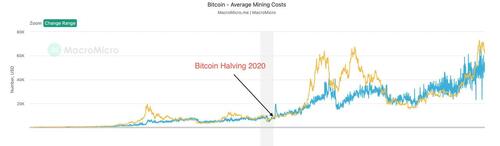
Each halving reduces the income that miners receive for verifying transactions, making profitability more challenging, especially for those with higher operational costs. This situation pressures miners to either upgrade to more efficient technology or cease operations.
For instance, after the third Bitcoin halving in May 2020, the average cost to mine one BTC rose, as the blue wave in the chart below illustrates.
The rise in operations costs squeezed smaller players out of the market, potentially increasing network centralization.
Pre-halving price rallies can be speculative
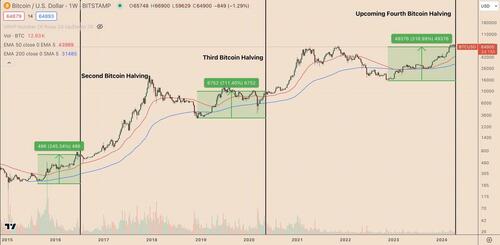
The anticipation of a Bitcoin halving often leads to speculative price increases.
For example, in the six months before the 2020 halving, Bitcoin's price increased by over 40%, from around $7,000 in November 2019 to approximately $10,000 by May 2020.
BTC/USD weekly price chart. Source: TradingView
These gains are often driven by speculative investors hoping to capitalize on the post-halving price increase, reflecting historical patterns and leading to volatility.
The theory behind a post-halving price increase is based on a supply shock. With each of the first three halvings, the daily production of Bitcoin decreased from 50 to 25 to 12.5, and most recently in 2020, to 6.25 BTC per block. This reduction can lead to significant price movements if demand remains strong.
For instance, the year following the 2016 halving saw a nearly 300% rise in Bitcoin's price, partly attributed to this supply shock.
Macroeconomic impact on Bitcoin halving cycles
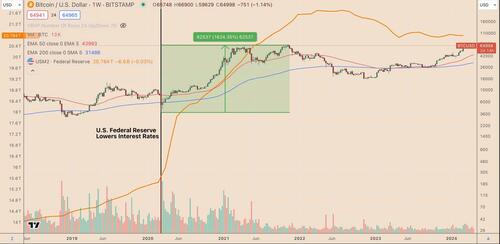
The broader economic environment plays a crucial role in shaping the impact of Bitcoin halvings on its price.
For example, the 2020 halving coincided with the period of loose monetary policies, including near-zero interest rates in the U.S. This unique situation contributed to Bitcoin's appeal as a "digital gold," helping its price to soar from around $8,000 at the time of the halving in May 2020 to an all-time high of nearly $69,000 by November 2021.
BTC/USD vs. U.S. M2 supply weekly performance chart. Source: TradingView
Last Bitcoin halving will occur next century
Thanks to the halving process, the final Bitcoin is projected to be mined around the year 2140. After the last halving, miners will no longer receive block rewards in new BTC but will rely solely on transaction fees for revenue.
This shift could fundamentally change Bitcoin's security and economic model, influencing everything from miner participation to transaction costs.
In summary, anticipation around halving events can increase demand for Bitcoin, potentially attracting new investors and boosting its visibility.
The cryptocurrency community may feel a sense of urgency and anticipation as a result of the halving. Around halving events, this increased attention frequently results in higher demand for Bitcoin and possible price swings.
Such market activity may pique people’s interest in Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies and raise public awareness of them, which could lead to increased adoption. Although the halving’s direct effect on price is speculative, BTC’s overall value proposition is strengthened within the evolving landscape of digital assets due to its role in highlighting its unique economic design.
Moreover, the emphasis on limited supply, controlled inflation and scarcity strengthens Bitcoin’s appeal as a competitive alternative to fiat currencies and other cryptocurrencies, potentially attracting a wider range of individual and institutional investors.
Every four years, the Bitcoin community celebrates the Bitcoin halving.
Many BTC market analysts view this as a quadrennial milestone event due to its historically bullish impact on the cryptocurrency market as a whole.
A key component of Bitcoin’s design is its periodic halving, which ensures the cryptocurrency’s scarcity and acts as a buffer against inflationary pressures.
Bitcoin halvings, which are programmed into Bitcoin’s code, occur about every four years. The block reward is halved with each halving event, and the supply of new Bitcoin (BTC) is directly impacted.
Additionally, halvings add to the intrinsic scarcity of Bitcoin by steadily lowering the rate at which new BTC enters the market. Its predictable and limited supply, which is capped at 21 million coins, supports Bitcoin’s long-term value proposition.
Halvings also reduce inflation by gradually decreasing the supply of new Bitcoin. This predictable inflation control mechanism makes Bitcoin a desirable alternative to conventional fiat currencies, which are vulnerable to unpredictable inflation.
As the market edges closer to Bitcoin’s fourth halving within hours, CoinTelegraph’s Yashu Gola dives into five fascinating facts about this phenomenon that even seasoned crypto-enthusiasts might not know.
Bitcoin price’s up over 650,000% since the first halving
Historically, Bitcoin’s price has increased following a halving, though this largely hinges on the balance of supply and demand.
Historical data provides some insights: After Nov. 28, 2012, the day of Bitcoin’s first halving, its price climbed from $11 to the then-record high of $1,240 a year later. Similarly, after the second halving in July 2016, Bitcoin’s price surged from around $650 to a new record high of $20,000 in December 2017.
In May 2020, after the third halving, Bitcoin’s price boomed from around $8,8000 toward $69,000 in November 2021. So, Bitcoin’s returns since the first halving stand at an astounding 650,000%.
Multiple catalysts have spurred demand for Bitcoin following its halving events. For instance, during 2020-2021, a generally dovish stance by global central banks significantly contributed to Bitcoin’s price rally.
Halvings test miners’ economic resilience
Each halving reduces the income that miners receive for verifying transactions, making profitability more challenging, especially for those with higher operational costs. This situation pressures miners to either upgrade to more efficient technology or cease operations.
For instance, after the third Bitcoin halving in May 2020, the average cost to mine one BTC rose, as the blue wave in the chart below illustrates.
The rise in operations costs squeezed smaller players out of the market, potentially increasing network centralization.
Pre-halving price rallies can be speculative
The anticipation of a Bitcoin halving often leads to speculative price increases.
For example, in the six months before the 2020 halving, Bitcoin’s price increased by over 40%, from around $7,000 in November 2019 to approximately $10,000 by May 2020.
BTC/USD weekly price chart. Source: TradingView
These gains are often driven by speculative investors hoping to capitalize on the post-halving price increase, reflecting historical patterns and leading to volatility.
The theory behind a post-halving price increase is based on a supply shock. With each of the first three halvings, the daily production of Bitcoin decreased from 50 to 25 to 12.5, and most recently in 2020, to 6.25 BTC per block. This reduction can lead to significant price movements if demand remains strong.
For instance, the year following the 2016 halving saw a nearly 300% rise in Bitcoin’s price, partly attributed to this supply shock.
Macroeconomic impact on Bitcoin halving cycles
The broader economic environment plays a crucial role in shaping the impact of Bitcoin halvings on its price.
For example, the 2020 halving coincided with the period of loose monetary policies, including near-zero interest rates in the U.S. This unique situation contributed to Bitcoin’s appeal as a “digital gold,” helping its price to soar from around $8,000 at the time of the halving in May 2020 to an all-time high of nearly $69,000 by November 2021.
BTC/USD vs. U.S. M2 supply weekly performance chart. Source: TradingView
Last Bitcoin halving will occur next century
Thanks to the halving process, the final Bitcoin is projected to be mined around the year 2140. After the last halving, miners will no longer receive block rewards in new BTC but will rely solely on transaction fees for revenue.
This shift could fundamentally change Bitcoin’s security and economic model, influencing everything from miner participation to transaction costs.
In summary, anticipation around halving events can increase demand for Bitcoin, potentially attracting new investors and boosting its visibility.
The cryptocurrency community may feel a sense of urgency and anticipation as a result of the halving. Around halving events, this increased attention frequently results in higher demand for Bitcoin and possible price swings.
Such market activity may pique people’s interest in Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies and raise public awareness of them, which could lead to increased adoption. Although the halving’s direct effect on price is speculative, BTC’s overall value proposition is strengthened within the evolving landscape of digital assets due to its role in highlighting its unique economic design.
Moreover, the emphasis on limited supply, controlled inflation and scarcity strengthens Bitcoin’s appeal as a competitive alternative to fiat currencies and other cryptocurrencies, potentially attracting a wider range of individual and institutional investors.
Loading…