Authored by Sophie Li via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
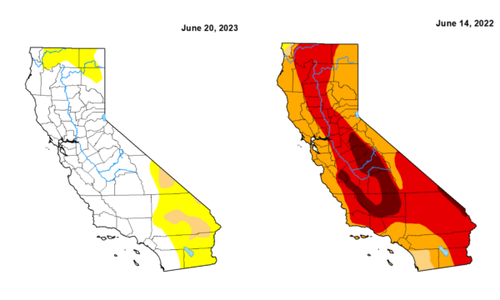
The historic barrage of storms this winter offered some breathing room for California’s extreme dry conditions, with 95 percent of the state now reported to be out of drought, according to the newest drought monitor map, from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and Climate Prediction Center, released June 13.

The update showed that now only about 5 percent of the state is in “moderate drought” and 27 percent is considered “abnormally dry.” Last year, the state was almost in 100 percent moderate-to-exceptional drought.
However, water experts say there is far more work ahead to prepare for future dry years.
“This one wet winter was not able to recharge our groundwater basins,” Darcy Burke, board director of Elsinore Valley Municipal Water District told The Epoch Times. “Water needs to slow down, needs to stay in place, and needs to slowly percolate through. We need more storage.”
According to Burke, over 26 million-acre-feet of water—enough for 75 million households—had to be released into the ocean between October and May this year.
Reservoirs are full, she said, and some water has been lost that was needed for other purposes.
“We have no place to put it,” she said. “[Lake] Oroville is full and it’s spilling. All the excess water … is going off the spillway not generating electricity.”

Water Flushed to Ocean as Reservoirs Overflowing
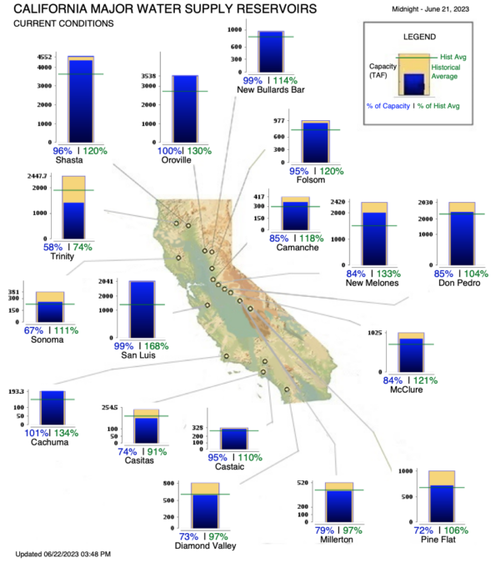
Lake Oroville, California’s second-largest reservoir, reached 100 percent capacity on June 6, with several others following, according to the California Department of Water Resources.
In contrast, in January, among the state’s 17 major reservoirs, only its smallest—the Cachuma Reservoir northwest of Santa Barbara—was nearly full, according to the water department. The rest were partially filled, ranging from about 30 to 80 percent.
According to the department, aging facilities made water storage and moving it through pipelines, canals, or ferries inefficient.
But some say the winter’s water was not stored because it was flushed to the ocean to help replenish some endangered fish species, like the Delta smelt.
“It’s a political problem,” Don Jackson, an almond farmer and a water board member of Kern County, said on a recent episode of EpochTV’s California Insider. “We’re flushing all the water out … instead of sending it to the people—which the aqueduct system was built for.”
Farmland Flooded but Pumping Still Restricted
A major part of California’s economy is agriculture, which generates over $50 billion in annual revenue and employs over 420,000 people, according to a study by the Public Policy Institute of California, a nonprofit research institution based in San Francisco.
While the rainfall eased the drought, it also flooded land, which is still not able to be used, said Burke from Elsinore Valley Municipal Water District.
Additionally, with so much flooded land, some dairy farmers were left with no place for their livestock.
“There’s no Motel Six to take a cow,” she said. “Tens of thousands of dairy cattle were either sold or were [slaughtered for food] because there was no place to put them.”
Read more here...
Authored by Sophie Li via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
The historic barrage of storms this winter offered some breathing room for California’s extreme dry conditions, with 95 percent of the state now reported to be out of drought, according to the newest drought monitor map, from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and Climate Prediction Center, released June 13.

The update showed that now only about 5 percent of the state is in “moderate drought” and 27 percent is considered “abnormally dry.” Last year, the state was almost in 100 percent moderate-to-exceptional drought.

However, water experts say there is far more work ahead to prepare for future dry years.
“This one wet winter was not able to recharge our groundwater basins,” Darcy Burke, board director of Elsinore Valley Municipal Water District told The Epoch Times. “Water needs to slow down, needs to stay in place, and needs to slowly percolate through. We need more storage.”
According to Burke, over 26 million-acre-feet of water—enough for 75 million households—had to be released into the ocean between October and May this year.
Reservoirs are full, she said, and some water has been lost that was needed for other purposes.
“We have no place to put it,” she said. “[Lake] Oroville is full and it’s spilling. All the excess water … is going off the spillway not generating electricity.”

Water Flushed to Ocean as Reservoirs Overflowing
Lake Oroville, California’s second-largest reservoir, reached 100 percent capacity on June 6, with several others following, according to the California Department of Water Resources.
In contrast, in January, among the state’s 17 major reservoirs, only its smallest—the Cachuma Reservoir northwest of Santa Barbara—was nearly full, according to the water department. The rest were partially filled, ranging from about 30 to 80 percent.
According to the department, aging facilities made water storage and moving it through pipelines, canals, or ferries inefficient.
But some say the winter’s water was not stored because it was flushed to the ocean to help replenish some endangered fish species, like the Delta smelt.
“It’s a political problem,” Don Jackson, an almond farmer and a water board member of Kern County, said on a recent episode of EpochTV’s California Insider. “We’re flushing all the water out … instead of sending it to the people—which the aqueduct system was built for.”

Farmland Flooded but Pumping Still Restricted
A major part of California’s economy is agriculture, which generates over $50 billion in annual revenue and employs over 420,000 people, according to a study by the Public Policy Institute of California, a nonprofit research institution based in San Francisco.
While the rainfall eased the drought, it also flooded land, which is still not able to be used, said Burke from Elsinore Valley Municipal Water District.
Additionally, with so much flooded land, some dairy farmers were left with no place for their livestock.
“There’s no Motel Six to take a cow,” she said. “Tens of thousands of dairy cattle were either sold or were [slaughtered for food] because there was no place to put them.”
Read more here…
Loading…