Authored by Iain Davis via Off-Guardian.org,
In Part 1, we discussed the historical background of Technocracy Inc. that briefly found popularity in the US in the 1930s during the turmoil of the Great Depression.
Technocracy was rooted in socioeconomic theories that focused upon the efficient management of society by experts (technocrats). This idea briefly held the public’s attention during a period of sustained recession, mass unemployment and growing poverty.
The technological capabilities required for the energy surveillance grid, essential for the operation of a Technate (a technocratic society), were far beyond the practical reach of 1930s America. Consequently, for that and other reasons, public interest in the seemingly preposterous idea of technocracy soon subsided.
However, in recent decades, many influential policy strategists—most notably Zbigniew Brzezinski and Henry Kissinger—and private philanthropic foundations, such as the Rockefeller Foundation, recognised that advances in digital technology would eventually make a Technate feasible. As founding and leading members of the Trilateral Commission, a policy “think tank,” they saw China as a potential test bed for technocracy.
We will now consider their efforts to create the world’s first Technate in China.
These articles build upon the research found in my 2021 publication Pseudopandemic, which is freely available to my blog subscribers.
WHY CHINA?
In the West we often have difficulty understanding or even conceptualising Chinese mores. We tend to see the world in our own terms and are able to describe it only in reference to the principles and philosophical concepts that we are familiar with. Perhaps we forget that the Western perspective is not the only one in the world.
For example, as pointed out by students of the Chinese political philosophy of tianxia, there is no ontological tradition in China. In the Chinese philosophical mind, the question is not “What is this thing” but “What path does this thing suggest?”
Datong lies at the heart of “the Great Way,” first described in the Liyun chapter of the “Book of Rites” (the Liji), written more than 2,000 years ago. Recounting the teachings of Confucius, the chapter depicted a utopian society of the ancient past this way:
When the Great Way was practised, the world was shared by all alike. The worthy and the able were promoted to office and men practised good faith and lived in affection. Therefore they did not regard as parents only their own parents, or as sons only their own sons.
The “Rites” (or “li”) are the formal etiquette and behavioural conduct that underpin Chinese social order. Li also compasses the ceremony and rituals that reinforce normative standards.
Datong, which can be translated as “the Great Unity,” represents the central political and moral philosophy of the ideal Chinese society. In datong, everyone respects “the li” and is imbued with the Confucian virtue of “ren.” This love and benevolence (ren) is founded in human empathy. It first manifests within the family but extends to the whole of society.
Datong implies a society where the most able and virtuous lead, with ren foremost in their hearts and minds. All resources are shared equitably for the common good. In the Liyun chapter, the expression “the world is shared by all alike” is written as “tianxia weigong.” This can be translated as “all under Heaven is held in common” or “all under Heaven is publicly held.”
There is no place for private property in datong, because communities meet the needs of all. There is no conflict of interest. The Great Way is one of “Universal Harmony.”
The opening passage of the Liyun chapter also described xiaokang, the “lesser prosperity,” in which society still maintained li and ren but differed from datong in an important regard:
The world is the possession of private families. Each regards as parents only his own parents, as sons only his own sons; goods and labour are employed for selfish ends.
While datong describes a world where resources are “shared by all alike,” in xiaokang resources are in “the possession of private families.” Xiaokang was not seen as opposed to datong but rather on the path toward it, for li and ren were still observed. But there is a warning in the Liyun chapter that private property and the control of resources by private interests present a risk:
Therefore intrigue and plotting come about and men take up arms.
Kang Youwei’s book “Datong shu” (The Great Commonwealth) was published posthumously in 1935. Kang wrote it as a series of lecture notes, the earliest dating to 1884. Rather than view datong only as a lost utopia, Kang proposed datong as a future society that could be constructed. He viewed ren as the path toward establishing the common good for all, attainable by eliminating suffering and creating happiness.
Kang noted that ren was applicable not only to humanity but to the universe and all within it, and he called this “jen.” Jen gave rise, he said, to creation and to the establishment of universal order. Therefore, order should be based upon the same principle of the “compassionate mind.”
He drew upon the work of the Confucian scholar He Xiu, whose Gongyang theory of history described sociopolitical development as a path consisting of incremental, progressive stages. Kang built upon Gongyang’s work to plot a course toward the Great Unity.
In essence, Kang suggested that society could be reverse-engineered to achieve datong in the future. He identified “nine boundaries” of human suffering that needed to be deconstructed in order to reach datong. He said that datong could be attained once nation-states, social class, racism, sexism, families, private property, injustice, environmental destruction, and poverty (the result of social inequality and oppression) were abolished.
“Sages” or “persons of jen” would be needed to lead, Kang maintained. He acknowledged that the sages had to operate in the social, economic and political circumstances of their day and that the resultant laws and institutions might be oppressive and cause suffering. Therefore, the objective of the “person of jen” (sage) should be to reform the laws and organisations of the state with a view to eradicating the nine boundaries of suffering.
With the abolition of the nation state, Kang’s proposed path toward the Great Way extended far beyond China. He favoured a global society where a world government would rule over a planet that was divided into regional districts.
In this global society, there would be no class or private property, and all would strive to deliver the common good and benefit everyone. Specifically, all resources would be deployed for the benefit and happiness of all. Public institutions, not families, would raise children. And the children would be trained to become citizens who would provide free services, such as health care and education, for all.
The only distinction between people would be the badges of honour worn by those deemed to have great ren, or knowledge—that is, the sages. Ultimately, once datong exists, there would be complete harmony with nature, which in turn would mean that all human beings are vegetarians and that euthanasia would be practised with ren, for the common good.
The ideology of datong, as Kang expounded it, and the hope of following the Great Way have strongly influenced Chinese political philosophy throughout the 20th and 21st centuries. Xi Jinping has been heard on numerous occasions to repeat the phrase, “When the Great Way prevails, the world is for everyone.”
Seen from the Chinese philosophical perspective, the best anyone can hope for today is xiaokang. Thus, xiaokang sages must be free to reform the institutions of the state on the path toward removing the nine boundaries, achieving datong and leading the Great Way.
There are many parallels between this path and the socioeconomic theory underpinning technocracy. For those who wished to establish a global technate, China was a natural choice for their pilot project.
UNDERSTANDING TECHNOCRACY
While there is a lot of debate about the extent of “legitimate” technocratic governance in the West’s supposedly liberal representative democracies, governance is just one aspect of technocracy. In other words, technocratic governance alone is not technocracy.
As discussed previously, a technocracy is a “governance of function.” The overarching goal is to run the whole of society as efficiently as possible.
The Technocracy Inc. Study Course states:
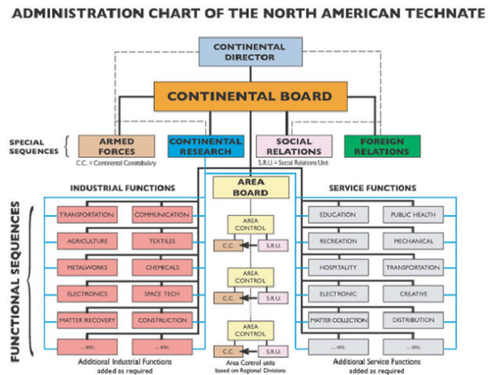
The basic unit of this organization is the Functional Sequence. A Functional Sequence is one of the larger industrial or social units, the various parts of which are related one to the other in a direct functional sequence. Thus among the major Industrial Sequences we have transportation (railroads, waterways, airways, highways and pipe lines); communication (mail, telephone, telegraph, radio and television); agriculture (farming, ranching, dairying, etc.); and the major industrial units such as textiles, iron and steel, etc. Among the Service Sequences are education (this would embrace the complete training of the younger generation), and public health (medicine, dentistry, public hygiene, and all hospitals and pharmaceutical plants as well as institutions for defectives)
Each “Functional Sequence” is overseen by a directorate. For example, the Distribution Sequence collects all the data gathered from the “Energy Certificates,” which are allocated to the citizens to be exchanged for goods and services. The “Price System” is abolished. There is no private property. The entire Technate is controlled by one body: Continental Control.
Like Kang’s “sages,” and in a fashion similar to guidance of the population toward the Great Way, a technocracy creates a rigid hierarchical structure to ensure that all are working for the common good. In the language of technocracy, the citizen contributes toward the appropriate service function.
Effectively, this creates a pyramid-like sociopolitical structure:
The personnel of all Functional Sequences will pyramid on the basis of ability to the head of each department within the Sequence, and the resultant general staff of each Sequence will be a part of the Continental Control. A government of function! The Continental Director, as the name implies, is the chief executive of the entire social mechanism. On his immediate staff are the Directors of the Armed Forces, the Foreign Relations, the Continental Research, and the Social Relations and Area Control. [. . .] The Continental Director is chosen from among the members of the Continental Control by the Continental Control. Due to the fact that this Control is composed of only some 100 or so members, all of whom know each other well, there is no one better fitted to make this choice than they.
Class is abolished in technocracy. Child care is provided by the Technate. Rather than having “great ren,” the general staff of the Technate are said to possess “peck-rights.” That is, they are the most suited to be at the top of the pyramid because a “governance of function” works most efficiently when “the right man is in the right place” to serve the common good.
Like the ideas presented in “Datong shu,” the intention of technocracy is essentially altruistic. The small cluster of engineers, economists, sociologists and other academics brought together by the Rockefellers and Howard Scott wanted to construct a society that would deliver “lives of abundance” to all.
It must be admitted that the Technocracy Inc. Study Course made some valid criticisms of a number of social problems. Unfortunately, the offered solution of a Technate is both arrogant and naïve.
It assumes, much as does the notion of a Great Way, that authority can be exercised by some human beings over other human beings for the common good. Further, it imagines that there is some social or political mechanism that can produce leaders who are omniscient and capable of defining what that “common good” is.
Both datong and technocracy would require human nature to undergo a fundamental transformation. Avarice, malevolence, narcissism, psychopathy and every other deleterious failing would need to be expunged from humanity. Until they are, power will continue to be sought by those who want to control others.
The most ruthless among us will ultimately succeed—often not because they are the most suited but because they are prepared to do what others won’t in order to gain the power they crave. This situation will persist for as long as we believe that someone or some organisation needs to have absolute authority over our lives in order for us to be able to cooperate effectively.
To imagine that concentrating all power in the hands of a tiny, select band of experts or sages will solve the problems caused by the unscrupulous and frequently violent and immoral use of authority is ridiculous. You can’t fix a kakistocracy by investing more power in the “kakistocrats.”
For the global public-private partnership (G3P), which operates a compartmentalised, hierarchical, pyramid-like power structure, the most enticing aspect of technocracy is the extreme centralisation of power and authority over vast swaths of the humanity. That is why, as soon as technological development permitted and the opportunity arose, the G3P set about assisting the development of a Technate in China.
INFILTRATING CHINA
The formal story of Henry Kissinger’s “secret” 1971 discussions with Chinese Premier Chou En-lai—officially acknowledged in 2001—is that US President Richard Nixon sent Kissinger to normalise relationships with the Chinese government as a counterbalance to the Soviet Union. What is mentioned less frequently, though, is Kissinger’s relationship with the Rockefellers.
In 1956, the Rockefeller Brothers Fund commissioned Kissinger to convene its Special Studies Panels. The panels investigated emerging global challenges and trends and suggested how US foreign policy might adapt to meet them.
In the 1961 publication of the six panel reports, Prospect for America (subtitled “The problems and opportunities confronting American democracy—in foreign policy, in military preparedness, in education, in social and economic affairs”), the Rockefeller Brothers Fund outlined how public-private partnership would be key to this projected future:
Corporations, whose operations extend through many nations[,] [. . .] through which a considerable and essential part of the world’s economic activities is carried on, must be able to compose diversities, adjust conflicts of interest, and adapt their operations to the needs of the country in which they operate. In doing so they represent a further example of multinational solutions to common problems.
The authors of these reports regarded private finance as essential not only for developing international markets but also for guiding the social and political development of the target nation:
Rapid economic growth can be achieved only if local savings and public foreign investment are supplemented by an increasing inflow of private foreign investment. Such investment performs two key functions: it adds to the capital resources of the host nation and it is the chief mechanism through which the managerial and technical skills and the creative and catalytic quality can contribute to economic development in less developed areas. [. . .] Private philanthropic capital can also play an important role in economic development.
The panels that provided the analysis for Prospect for America were convened in the aftermath of McCarthyism. They needed to appeal to a US polity still obsessed with the perceived threat of international communism. Thus, the reports eulogise so-called democracy throughout.
However, there are numerous indications that the Rockefeller foreign policy strategists were willing to diplomatically suggest alternatives:
The American pattern of private enterprise and voluntary association is not the only mold for a free society.
It is clear that these strategists sought to both exploit the differences between nation-states for their development potential and amplify the importance of global issues as a means of uniting nations, regardless of their model of government, under a system of global governance. They considered scientific and technological development one way to do just that:
In the field of science, international cooperation on a world scale is most readily achievable. [. . .] [T]he United States should, therefore, seek to develop a series of agreements, looking toward the stimulation of scientific interchange and the fostering of scientific progress on a world scale. [. . .] The Communist nations should be invited to participate.
The panels, which effectively formed a temporary Rockefeller-funded think tank, were not opposed to colonialism on moral grounds but they highlighted its tactical flaws. Inherent in their critique of colonialism was an acknowledgement that alleged democratic values have nothing to do with hard-nosed geopolitics or with expansive foreign policy ambitions:
While colonialism exacted a human and political toll, it also represented one of the greatest conversions in history. As the ideals of the British, French and American revolutions became diffused, partly through the very spread of colonialism, the seeds were sown for the destruction of colonialism itself. The more successful the teachings of the colonial powers, the more untenable grew their position. Almost without exception, the leaders of independence movements fought their rulers in terms of the rulers’ own beliefs. They asked them to live up to their own principles.
The Rockefellers, being one of the leading families at the head of the G3P’s compartmentalised hierarchy, had worked with the Chinese authorities for generations. John D. Rockefeller Sr. was trading kerosene in China in 1863.
The family’s philanthropic foundation had long fostered strong ties with the Chinese government. For example, it helped advance the use of Western allopathic medicine in China by establishing the Peking Union Medical College (PUMC) and by making other philanthropic investments.
It’s safe to say that the Rockefellers were knowledgeable and enthusiastic supporters of the Chinese government. Not surprisingly, they were also knowledgeable and enthusiastic supporters of the technocracy movement in the US, maintaining their keen interest in it despite its lack of public support. They understood the potential of social engineering to create a governance of function (a Technate):
Changes in technology have always been a major cause of change in government, economic relations and social institutions. But technological innovation is no longer the work of isolated, ingenious inventors; it is the product of organised scientific enterprise and is constant, insistent and accelerating. One of its notable effects is upon the tempo of social change itself, which is enormously quicker than it has been, and which subjects every inhabitant of a technological society to its pressures. Technological innovation thus poses a series of issues with which our society will have to deal. [. . .] The growth of technological society has changed the traditional society in which men have enjoyed freedom. Large and complex organisations have become the order of the day. [. . .] Programs for the preservation and strengthening of individual freedom must assume the existence and the inevitability of such organisations.
The Rockefellers had a nuanced appreciation of the potential for technological development to act as the catalyst for change. Despite the report’s primary focus on the US relationship with the Soviet Union, the Rockefellers obviously recognised the ripe opportunities in China:
It [China] has a rapidly growing population, a shortage of resources, and a fanatical ideology. Around a large part of its perimeter exists “soft” situations, making infiltration, subversion, and outright conquest seem easy or inviting prospects. The present relations between Soviet Russia and Red China [. . .] may not always be drawn together by common interests. [. . .] We must avoid, wherever possible, courses that seem to drive China closer to the Soviets.
As founders of the Trilateral Commission, the Rockefellers’ and their fellow Trilateralists’ goal was to infiltrate China by extending the hand of cooperative friendship through public-private investment in technological and thus financial and economic development.
The Sino-Soviet split was seemingly the window of opportunity they wished to lever open.
China’s society, its political history and government structure was already amenable to the introduction of technocracy, as it was to communism. The Trilateralists were apparently eager to avoid the mistakes of Western colonialists, who extolled the democratic ideals and associated legal concepts which had come back to bite them. These ideals were, in any event, antithetical to the Trilateralists’ project.
ASSISTING CHINA
Following Mao’s death in 1976, Deng Xiaoping rose to power, becoming the Paramount Leader of the People’s Republic of China (PRC) in 1978. Just two weeks after assuming power, on January 1, 1979, he became the first communist Chinese leader to conduct a formal state visit to the US.
He was received with full state honours by the administration of Jimmy Carter, whose National Security advisor was Trilateralist Zbigniew Brzezinski—and who was himself a Trilateralist.
Deng Xiaoping immediately set about instigating a series of social and economic reforms, which were called “reform and opening up” in China and “the opening up of China” in the West.
Deng was one of a group of eight high-ranking Chinese officials who had survived the brutal repressions of cultural revolution. The reverently named “Eight Immortals” were credited with turning the Chinese economy from an unstable mess, riven with extreme poverty, into the thriving economic engine it is today.
Despite the hopes of datong, and far from being the sages that Kang Youwei dreamed of, the sons and daughters of the Eight Immortals, who are collectively known as the Princelings, hoovered up China’s state assets to effectively create a new dynasty, just as corrupt as its predecessors. Such is the nature of kakistocracy.
The scale and pace of the economic transformation in such a vast country would have been impossible without the considerable inward investment and the transfer of technology which China received from the G3P. This G3P investment was the initial source of China’s economic growth miracle. In late 2019, The World Economic Forum (WEF) reported:
High levels of government spending and foreign investment have enabled China to roughly double the size of its economy every eight years since the introduction of economic reforms in 1979.
CITIC (China International Trust & Investment Corp, renamed CITIC Group) was effectively China’s state–run investment arm. Kissinger’s visit to China had opened up investment banking opportunities for Rockefeller’s Chase Group (Chase Manhattan Bank at the time.)
In June 1980, CITIC Chairman Rong Yiren attended a meeting with David Rockefeller and the representatives of 300 Fortune 500 companies in the Chase Manhattan offices in New York.
The purpose of the meeting between CITIC and the G3P representatives was:
[To] identify and define those areas of the Chinese economy most susceptible to American technology and capital infusion.
Kissinger and Rong reportedly established an investment company, with Trilateralist Kissinger appointed as a special advisor to CITIC. The initial phase of China’s economic transformation consisted of banking reforms that allowed much greater Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in China.
FDIs aren’t just capital investments. They typically come with a transfer or sharing of expertise, technology and even workforce. Common types of FDIs are mergers, acquisitions, management services and logistical and manufacturing agreements.
From the mid 1980s onwards the G3P began to pour into Beijing’s Central Business District (CBD).
By 2009 there were 114 Western companies with a substantial presence and established investments in Beijing and beyond. By 2020 there were 238 Fortune 500 companies in Beijing. Today, Beijing CBD (called the Functional Area) now houses the regional headquarters of 105 multinational corporations and more than 4,000 foreign-invested enterprises. The CBD is one of six “high-end industrial functional areas in Beijing.”
According to Chinese state media, between 1983 and 1991 FDI in China went from a value of $920 million to $4.37 billion. By 2019 total FDI had risen to more than $2.1 trillion. At the same time, the transition economy of China, just like many other economies, rapidly expanded its money supply.
All of this monopoly money, a mixture of FDI and domestic (digital) currency printing, fuelled the economic and technological development of China. In exchange for access to its market, the Chinese government required that investors sign so-called Forced Technology Transfer (FTT) agreements.
Simultaneously, the Western mainstream media (MSM) began constantly pushing the notion of the “rising threat” of China and frequently accused China of alleged industrial espionage and “technology theft.“
Like so much propaganda aimed at Western populations by their MSM, these charges were just a fabrication. In truth, no one was forcing anyone to transfer technology to China. In fact, Trilateralists like President Bill Clinton went to considerable lengths to make sure China could get hold of the technology, including military technology, it needed.
In 1994 the Clinton administration scrapped Cold War export controls, thereby enabling more sensitive technology to be transferred to China. Claiming that they would not allow defence technology, such as supercomputer or potential uranium enrichment technology, to go to China (or Russia), they soon lifted this restriction via a work-around that shifed oversight from the departments of State and Defense to the Department of Commerce.
One only has to look at the near identical design of US and Chinese defence systems and weaponry to see that a massive amount of “sensitive” technology is common to both countries.
The asinine explanation we are given is that this is all the result of Chinese espionage, even though the US government has amended legislation to make such transfers possible.
The Israeli government and Israeli defence contractors have consistently acted as facilitators for the transfer of the most sensitive Western defence and surveillance technology to China. As soon as “reform and opening up” began in 1979, Israeli multibillionaire—then a humble billionaire—Saul Eisenberg flew a delegation of defence contractors to arrange military supply contracts with the Chinese government.
While the West’s MSM parrots the intelligence agencies’ overwhelmingly baseless claims that China represents an “immense threat,” the US government and others have maintained deep defence ties with the Israeli government for generations.
In the full and certain knowledge that Israel is passing defence technology to China, the US and other NATO allies continue to provide Israel with the latest defence technology.
Occasionally a story surfaces claiming that Washingtion is “angered” by this habitual practice. If we look beyond the propaganda, the fables simply reaffirm that which is blatantly obvious.
The Israeli government, its defence contractor and tech corporation partners, have consistently acted as a conduit for the transfer of “sensitive” defence, fintech, surveillance and communication technology from the West to China. Between 1992 and 2017 the volume of overall trade between Israel and China multiplied 200 times over.
Another Western propagandist myth is that China has “stolen” jobs from Western economies. While it is true that manufacturers took advantage of cheaper labour costs in China, leading to job losses in the West, the practice of offshoring jobs had been ongoing for decades.
Companies are in the business of maximising profits for shareholders and staying competitive. No one was forcing Western corporations to offshore. It was simply an economic expediency, largely the consequence of G3P efforts to modernise China’s economy.
Often the focus of G3P investment in China has been Research and Development (R&D). In 1994 China ranked 30th in terms of US overseas R&D investment; by 2000 it was 11th.
Between 1994 to 2001 multinational corporation (MNC) investment in China quadrupled. As a ratio of overseas R&D investment, the G3P were providing thrice the amount of “technology infusion” into China compared to anywhere else.
While the pseudopandemic sharpened the decline in total global FDI, that figure continued to rise in China.
The 4% increase of FDI in China in 2020 saw it temporarily surpass the US as the world’s leading recipient of direct investment. In 2020, while FDI in other advanced economies collapsed, China benefited from FDI valued at $163 billion.
In addition to the huge growth stimulus pumped into the Chinese economy over the last four decades, a significant number of foreign/Chinese industrial R&D alliances were established. These were separate business organizations that targeted specific research or technological development projects. They were formed through collaboration between academic and scientific research establishments, NGOs, government institutions and private enterprise.
Between 1990 and 2001 the US government established 105 such alliances. In the same time period, Japan had the second largest number of R&D partnership alliances (26), followed by Germany (15), the UK (14), Singapore (12), and Canada (11). The overwhelming majority of these R&D collaborations operated in China.
From 2001, to the financial crash in 2008, both FDI in R&D and China’s own R&D investment really took off. While the explosive pace of FDI growth slowed from 2010 onward, by 2016 China’s own outward foreign investment had surpassed the FDI it received. That was an astounding economic turnaround in less than 40 years.
A 2019 report by the World Bank stated:
China’s spending on research and development (R&D) rose to 2.18 percent of GDP in 2018, up from 1.4 percent in 2007[.] [. . .] Its spending on R&D accounts for around 20 percent of the world total, second only to the United States. Its number of patents granted annually for inventions increased from 68,000 in 2007 to 420,000 in 2017, the highest in the world. [. . .] China is also a hotbed for venture capital in search of the next technology. [. . .] China has evolved from being a net importer of FDI to a net exporter. [. . .] China remains an attractive destination for foreign investments due to its large domestic market. Foreign enterprises such as BASF, BMW, Siemens, and Tesla have recently announced new or expanded investments in China.
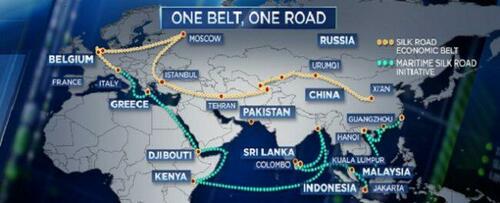
A focus of apparent Western concern has been China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
This enormous infrastructure project, known in China as One Belt, One Road, or OBOR, is establishing a network of modern trade routes across Eurasia, linking Asia, Africa, Europe, South East Asia and Australasia, easing both international trade and, in particular, Chinese exports.
Beyond China’s borders there are 140 countries involved in the BRI to one degree or another.
In its 2018 research paper looking at FDI in a BRI-related project, the World Bank referred to those countries directly involved in its construction as BRI nations. China’s own investment in BRI nations has grown, but the majority of its FDI goes to non-BRI nations. These, according to the World Bank, are nations that are not inviolved in the BRI.
China is the leading single nation investor in BRI nations but it does not account for the bulk of total investment. China took the lead after the 2008 financial crisis saw non-BRI nations (such as the US and the UK) pull back on their FDI deals in BRI nations. The investment from the non-BRI nations picked up again as quantitative easing (money printing) monetary policies in Western countries took effect post-2010.
The World Bank reported:
The majority of BRI countries’ [those who are part of the One Belt, One Road project] FDI inflow comes from non-BRI countries.
That is to say, BRI nations—Italy, Saudi Arabia, Austria, New Zealand, South Korea and Singapore, etc.—are net recipients of FDI from non-BRI nations, such as the US, UK, France and Germany.
The majority of the investment, expertise and technology that is building the BRI infrastructure comes from the non-BRI G3P partners. The notion that Western politicians, corporations and financial institutions are worried about the Belt and Road Initiative is just an MSM story. In reality, they are working hard to construct it in partnership with China.
CHINA: THE WORLD’S FIRST TECHNATE
China has developed an overt system dedicated to the social engineering of society.
As noted in Part 1, the definition of technocracy is:
The science of social engineering, the scientific operation of the entire social mechanism to produce and distribute goods and services to the entire population.
The focus of technocracy is to direct the population to maximise the efficiency of all “functions” of society, primarily through control of the allocation of resources.
Published in 2014, the State Council Notice for planning a Social Credit System (SCS) outlined the Chinese government’s rationale for its social credit system:
The social credit system is an important component of the Socialist market economy system and the social governance system; [. . .] its foundation is a complete network covering the credit records of all members of society and the credit infrastructure; [. . .] its reward and punishment mechanisms are incentivizing trustworthiness and restricting untrustworthiness. [. . .] The establishment of a social credit system is an important foundation for comprehensively implementing the scientific viewpoint of development. [. . .] Accelerating and advancing the establishment of the social credit system is an important precondition for promoting the optimized allocation of resources.
This is a description of pure technocracy.
Western commentators often focus upon the technological aspects of China’s social credit system. China certainly operates a dystopian surveillance society, but this complements the social credit system which, as the name suggests, is an overarching system for “implementing the scientific viewpoint of development.”
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) reported that the supposedly “terrifying system doesn’t exist” in China:
[T]he system that the central government has been slowly working on is a mix of attempts to regulate the financial credit industry, enable government agencies to share data with each other, and promote state-sanctioned moral values.
MIT and its funding partners, such as the Rockefeller Foundation, have consistently highlighted the potential merits of the social credit system (SCS).
When reading that material, we must separate the rhetoric of the engineers of the social credit system from its practical application.
Like the Great Way or technocracy or communism, the political philosophy underpinning the social credit system is presented by its advocates as progressive, humanitarian and benign. Naturally, the people who impose this system would also need to be progressive, humanitarian and benign, right?
Yet, while the social credit system is effectively a massive bureaucracy, combining the digital sharing of information with legislation and various paper-shuffling exercises, there are many aspects of it that are extremely concerning.
For one thing, it creates a public-private partnership that, by rewarding good behaviour, fosters public faith in the mechanisms of the state. For another, it punishes those who aren’t duly faithful.
The SCS removes access to “privileges” from people who have broken the law and even from those who haven’t. The concept of Joint Disciplinary Action in the SCS introduces the idea that, if found “untrustworthy,” a citizen or organisation so labelled will face broader social consequences, from having their right to fly removed to restricting their ability to book “high-class” tickets on trains to impeding their employment or business opportunities.
The SCS sets up a blacklist for those deemed to have committed “misdeeds.” Thus far it has predominantly punished those who have failed to pay court fines or those considered bad debtors.
Chinese state media have praised the courts’ partnership with tech giants like Sesame Credit—the credit-scoring system of the Alibaba Group subsidiary Ant Financial.
Chinese government data, gathered from the courts and elsewhere, has been combined with private data, gathered from social media, for the purpose of lowering the financial credit score of millions of people who have been “blacklisted.”
Public humiliation and shaming are commonly used to change the blacklisted’s behaviour. The Supreme Court maintains a database of “discredited individuals” (laolai). Tech companies like TikTok, owned by Chinese company ByteDance Ltd., publish laolai lists from the publicly available data to inform its users which companies and individuals have been “discredited.”
Technology enhances the social credit system.
To register a SIM cards and new SMART phones, Chinese users must by law use face scan technology. This biometric data then informs China’s already extensive and rapidly expanding national network of facial recognition cameras.
The surveillance grid, allowing entry to everything from bus depots to safari parks, is integrating with alleged emotion-recognition technology to assess an individual’s mood and “predict” their behaviour.
China’s internet is highly regulated via the “Measures on the Administration of Internet Information Services.” The government prohibits news bloggers from commenting on any policies or political developments without a license from the Cyberspace Adminstration of China (CAC).
Again, this system operates as a public-private partnership. There are eight licensed Internet Service Providers (ISPs) in China registered with the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT), but censorship largely occurs through the state’s partnership with fintech companies and social media platforms. The censorship is overseen by the Internet Information Office.
The Chinese have to register their personal details to use the popular social media platforms. The independent sale of SIM cards and network adapters is prohibited; the cards and adapters require similar registration upon purchase and prior to use.
The Chinese authorities can block foreign websites, restricting citizens access to information from outside China, and it is a crime for anyone to facilitate the illegal flow of prohibited information into China. The Chinese authorities have effectively created the crime of information-smuggling.
Beyond inciting crimes or advocating violence or terrorism, Article 12 of China’s Cybersecurity Law outlines the other types of information that Chinese people are not permitted to share:
[Users] must not use the Internet to engage in activities endangering national security, national honour, and national interests; they must not incite subversion of national sovereignty, overturn the socialist system, incite separatism, break national unity, [. . .] create or disseminate false information to disrupt the economic or social order, or information that infringes on the reputation, privacy, intellectual property or other lawful rights and interests of others, and other such acts.
In other words, no one is permitted to question the state in China. This doesn’t stop the people from doing so, but the associated risks are high. Political dissidents can certainly expect to be censored by the social media platforms, and prison sentences are a distinct possibility for those who speak out too vociferously.
Among the major geopolitical powers, China is leading in the development of Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC). CBDC is “programmable money” and the issuer can insert “smart contracts” to control what can be bought, where it can be used and who can use it.
Bo Li, the former Deputy Governor of the Bank of China and the current Deputy Managing Director of the International Monetary Fund (IMF), speaking at the Central Bank Digital Currencies for Financial Inclusion: Risks and Rewards symposium, clarified smart contracts further:
CBDC can allow government agencies and private sector players to program [CBDC] to create smart-contracts, to allow targetted policy functions. For example[,] welfare payments [. . .], consumptions coupons, [. . .] food stamps. By programming, CBDC money can be precisely targeted [to] what kind of [things] people can own, and what kind of use [for which] this money can be utilised. For example, [. . .] for food.
At the 2022 World Economic Forum’s Davos gathering, the president of the Chinese Alibaba Group, J. Michael Evans, announced that the global tech corporation would soon roll out its personal “carbon footprint tracker.”
He said:
We’re developing, through technology, an ability for consumers to measure their own carbon footprint [. . .] That’s where they’re travelling, how they are travelling, what are they eating, what are they consuming on the platform. [. . .] So, individual carbon footprint tracker, stay tuned! We don’t have it operational yet, but this is something we’re working on.
During the initial COVID-19 lockdowns, China’s government required all businesses and public services to install Covid status app scanners, connected to the internet.
In order to access shops, restaurants, libraries, hospitals, etc., and to move between the newly created urban “zones,” the Chinese have to use their Covid app. In conjunction with the SIM and SMART phone registration requirements, combined with the biometric facial recognition technology, the public movements of the urban Chinese can be tracked 24/7 in real time by China’s public-private partnership.
The foundations for “the scientific operation of the entire social mechanism” have already been built in China. One of the major cities conducting some of its business in CBDC is Shanghai. In Shanghai’s Pudong “smart city” district, an AI integrated monitoring system is able to access the feeds from 290,000 surveillance cameras.
The deputy director of the smart city, Sheng Denden, explained the systems value to the Chinese government:
For the government, this is a tool for more efficient administration in the city.
China is not communist. It is a technocracy. It is the world’s first Technate.
THE CHINA BLAME GAME
As we have already discussed, the idea that Western governments are “opposed” to China’s government is frankly ridiculous. This is not to suggest that there aren’t tensions, but these spring from competition not trenchant animosity. China’s government, and its tech giant partners, are as much a part of G3P as any other nation. The propaganda, from both the West and the Communist Party of China, serves as a surface narrative designed to divide and rule the global population, and to exert control over the respective domestic populations.
The Trilateralists who worked tirelessly to ensure that China was able to construct a Technate are seemingly proud of their claimed achievements. In 2001, Hedley Donovan, one of the founding members of the Trilateral Commission alongside Brzezinski and the Rockefellers, wrote:
It’s no exaggeration to describe the current regime as a technocracy. [. . .] You might say that technocratic politics is a natural fit with the Chinese political culture. [. . .] During the 1980s, technocracy as a concept was much talked about, especially in the context of so-called ‘Neo-Authoritarianism.’ [. . .] The basic beliefs and assumptions of the technocrats were laid out quite plainly: Social and economic problems were akin to engineering problems and could be understood, addressed, and eventually solved as such. [. . .] Scientism underlies the post-Mao technocracy, and it is the orthodoxy against which heresies are measured.
The self-congratulation was largely misplaced. That China’s government developed a Technate owes more to that nation’s circumstances and political and social history and belief systems than it does to the ambitions of the Trilateralists.
Technocracy is intended to be a sociopolitical system where individual rights are sacrificed to communitarianism. This is contrary to the Western liberal tradition. Technocracy represented less of a culture shock to the Chinese people. Certainly this fact was another impetus for the Trilateralists to pilot technocracy in China.
Just as we in the West generally believe in individual liberty and freedom from the state, so the Chinese people largely hold that the state should strive to rule with ren along the path to the Great Way and equality for all. In both cases, the people continue to be deceived and disappointed by the “kakistocrats,” who clearly have no intention of living up to any of those principles or expectations.
The mass and widespread Chinese demonstrations against the human cost of the government’s harsh Covid lockdown measures shows that the people are not willing to simply allow the state to do whatever it likes.
While isolated protests in China are not unusual, the scale and coordination of these protests are testament to the Chinese people’s determination to resist oppression.
The Western investment in Chinese technocracy was made with a view to developing a global system, not one restricted to China. From the surveillance network and social credit to censorship and social control using CBDC, having seen what can be achieved in China, Western governments are busy trying to impose exactly the same model of technocracy upon their own people.
The Western political class cannot help but openly admire China’s technocracy. The only difference is that China’s system is publicly discussed—although rarely acknowledged as “technocracy” by name—while the rapidly emerging technocracy in the West is denied and concealed.
The G3P is ostensibly colonising Western populations yet remains eager to avoid the errors of 19th century colonialists. The Rockefellers’ research in the late 1950s highlighted the need to first justify the necessary destruction of democratic values—something all Western governments are working hard to do.
For its part, the Chinese government has had its own reasons for allowing technocracy to flourish. Technocracy fits well with China’s domestic policy ambitions. That said, there is no reason to think that the Chinese government ever intended to “export” technocracy to other nations.
Technocracy is being installed globally. This suits China’s oligarchy, accustomed as it is to operating a Technate. The Chinese government has no reason to stand in the way of the global adoption of technocracy. It is merely aligned with the global transformation, not leading it.
China’s government is not forcing other nations to adopt technocracy. Rather, all governments are collaborating to that end.
The Chinese people are not our enemy, and China is not a foe to be fought. We, the people of the Earth, are all under attack by our own G3P governments.
Authored by Iain Davis via Off-Guardian.org,
In Part 1, we discussed the historical background of Technocracy Inc. that briefly found popularity in the US in the 1930s during the turmoil of the Great Depression.
Technocracy was rooted in socioeconomic theories that focused upon the efficient management of society by experts (technocrats). This idea briefly held the public’s attention during a period of sustained recession, mass unemployment and growing poverty.
The technological capabilities required for the energy surveillance grid, essential for the operation of a Technate (a technocratic society), were far beyond the practical reach of 1930s America. Consequently, for that and other reasons, public interest in the seemingly preposterous idea of technocracy soon subsided.
However, in recent decades, many influential policy strategists—most notably Zbigniew Brzezinski and Henry Kissinger—and private philanthropic foundations, such as the Rockefeller Foundation, recognised that advances in digital technology would eventually make a Technate feasible. As founding and leading members of the Trilateral Commission, a policy “think tank,” they saw China as a potential test bed for technocracy.
We will now consider their efforts to create the world’s first Technate in China.
These articles build upon the research found in my 2021 publication Pseudopandemic, which is freely available to my blog subscribers.
WHY CHINA?
In the West we often have difficulty understanding or even conceptualising Chinese mores. We tend to see the world in our own terms and are able to describe it only in reference to the principles and philosophical concepts that we are familiar with. Perhaps we forget that the Western perspective is not the only one in the world.
For example, as pointed out by students of the Chinese political philosophy of tianxia, there is no ontological tradition in China. In the Chinese philosophical mind, the question is not “What is this thing” but “What path does this thing suggest?”
Datong lies at the heart of “the Great Way,” first described in the Liyun chapter of the “Book of Rites” (the Liji), written more than 2,000 years ago. Recounting the teachings of Confucius, the chapter depicted a utopian society of the ancient past this way:
When the Great Way was practised, the world was shared by all alike. The worthy and the able were promoted to office and men practised good faith and lived in affection. Therefore they did not regard as parents only their own parents, or as sons only their own sons.
The “Rites” (or “li”) are the formal etiquette and behavioural conduct that underpin Chinese social order. Li also compasses the ceremony and rituals that reinforce normative standards.
Datong, which can be translated as “the Great Unity,” represents the central political and moral philosophy of the ideal Chinese society. In datong, everyone respects “the li” and is imbued with the Confucian virtue of “ren.” This love and benevolence (ren) is founded in human empathy. It first manifests within the family but extends to the whole of society.
Datong implies a society where the most able and virtuous lead, with ren foremost in their hearts and minds. All resources are shared equitably for the common good. In the Liyun chapter, the expression “the world is shared by all alike” is written as “tianxia weigong.” This can be translated as “all under Heaven is held in common” or “all under Heaven is publicly held.”
There is no place for private property in datong, because communities meet the needs of all. There is no conflict of interest. The Great Way is one of “Universal Harmony.”
The opening passage of the Liyun chapter also described xiaokang, the “lesser prosperity,” in which society still maintained li and ren but differed from datong in an important regard:
The world is the possession of private families. Each regards as parents only his own parents, as sons only his own sons; goods and labour are employed for selfish ends.
While datong describes a world where resources are “shared by all alike,” in xiaokang resources are in “the possession of private families.” Xiaokang was not seen as opposed to datong but rather on the path toward it, for li and ren were still observed. But there is a warning in the Liyun chapter that private property and the control of resources by private interests present a risk:
Therefore intrigue and plotting come about and men take up arms.
Kang Youwei’s book “Datong shu” (The Great Commonwealth) was published posthumously in 1935. Kang wrote it as a series of lecture notes, the earliest dating to 1884. Rather than view datong only as a lost utopia, Kang proposed datong as a future society that could be constructed. He viewed ren as the path toward establishing the common good for all, attainable by eliminating suffering and creating happiness.
Kang noted that ren was applicable not only to humanity but to the universe and all within it, and he called this “jen.” Jen gave rise, he said, to creation and to the establishment of universal order. Therefore, order should be based upon the same principle of the “compassionate mind.”
He drew upon the work of the Confucian scholar He Xiu, whose Gongyang theory of history described sociopolitical development as a path consisting of incremental, progressive stages. Kang built upon Gongyang’s work to plot a course toward the Great Unity.
In essence, Kang suggested that society could be reverse-engineered to achieve datong in the future. He identified “nine boundaries” of human suffering that needed to be deconstructed in order to reach datong. He said that datong could be attained once nation-states, social class, racism, sexism, families, private property, injustice, environmental destruction, and poverty (the result of social inequality and oppression) were abolished.
“Sages” or “persons of jen” would be needed to lead, Kang maintained. He acknowledged that the sages had to operate in the social, economic and political circumstances of their day and that the resultant laws and institutions might be oppressive and cause suffering. Therefore, the objective of the “person of jen” (sage) should be to reform the laws and organisations of the state with a view to eradicating the nine boundaries of suffering.
With the abolition of the nation state, Kang’s proposed path toward the Great Way extended far beyond China. He favoured a global society where a world government would rule over a planet that was divided into regional districts.
In this global society, there would be no class or private property, and all would strive to deliver the common good and benefit everyone. Specifically, all resources would be deployed for the benefit and happiness of all. Public institutions, not families, would raise children. And the children would be trained to become citizens who would provide free services, such as health care and education, for all.
The only distinction between people would be the badges of honour worn by those deemed to have great ren, or knowledge—that is, the sages. Ultimately, once datong exists, there would be complete harmony with nature, which in turn would mean that all human beings are vegetarians and that euthanasia would be practised with ren, for the common good.
The ideology of datong, as Kang expounded it, and the hope of following the Great Way have strongly influenced Chinese political philosophy throughout the 20th and 21st centuries. Xi Jinping has been heard on numerous occasions to repeat the phrase, “When the Great Way prevails, the world is for everyone.”
Seen from the Chinese philosophical perspective, the best anyone can hope for today is xiaokang. Thus, xiaokang sages must be free to reform the institutions of the state on the path toward removing the nine boundaries, achieving datong and leading the Great Way.
There are many parallels between this path and the socioeconomic theory underpinning technocracy. For those who wished to establish a global technate, China was a natural choice for their pilot project.
UNDERSTANDING TECHNOCRACY
While there is a lot of debate about the extent of “legitimate” technocratic governance in the West’s supposedly liberal representative democracies, governance is just one aspect of technocracy. In other words, technocratic governance alone is not technocracy.
As discussed previously, a technocracy is a “governance of function.” The overarching goal is to run the whole of society as efficiently as possible.
The Technocracy Inc. Study Course states:
The basic unit of this organization is the Functional Sequence. A Functional Sequence is one of the larger industrial or social units, the various parts of which are related one to the other in a direct functional sequence. Thus among the major Industrial Sequences we have transportation (railroads, waterways, airways, highways and pipe lines); communication (mail, telephone, telegraph, radio and television); agriculture (farming, ranching, dairying, etc.); and the major industrial units such as textiles, iron and steel, etc. Among the Service Sequences are education (this would embrace the complete training of the younger generation), and public health (medicine, dentistry, public hygiene, and all hospitals and pharmaceutical plants as well as institutions for defectives)
Each “Functional Sequence” is overseen by a directorate. For example, the Distribution Sequence collects all the data gathered from the “Energy Certificates,” which are allocated to the citizens to be exchanged for goods and services. The “Price System” is abolished. There is no private property. The entire Technate is controlled by one body: Continental Control.
Like Kang’s “sages,” and in a fashion similar to guidance of the population toward the Great Way, a technocracy creates a rigid hierarchical structure to ensure that all are working for the common good. In the language of technocracy, the citizen contributes toward the appropriate service function.
Effectively, this creates a pyramid-like sociopolitical structure:
The personnel of all Functional Sequences will pyramid on the basis of ability to the head of each department within the Sequence, and the resultant general staff of each Sequence will be a part of the Continental Control. A government of function! The Continental Director, as the name implies, is the chief executive of the entire social mechanism. On his immediate staff are the Directors of the Armed Forces, the Foreign Relations, the Continental Research, and the Social Relations and Area Control. [. . .] The Continental Director is chosen from among the members of the Continental Control by the Continental Control. Due to the fact that this Control is composed of only some 100 or so members, all of whom know each other well, there is no one better fitted to make this choice than they.
Class is abolished in technocracy. Child care is provided by the Technate. Rather than having “great ren,” the general staff of the Technate are said to possess “peck-rights.” That is, they are the most suited to be at the top of the pyramid because a “governance of function” works most efficiently when “the right man is in the right place” to serve the common good.
Like the ideas presented in “Datong shu,” the intention of technocracy is essentially altruistic. The small cluster of engineers, economists, sociologists and other academics brought together by the Rockefellers and Howard Scott wanted to construct a society that would deliver “lives of abundance” to all.
It must be admitted that the Technocracy Inc. Study Course made some valid criticisms of a number of social problems. Unfortunately, the offered solution of a Technate is both arrogant and naïve.
It assumes, much as does the notion of a Great Way, that authority can be exercised by some human beings over other human beings for the common good. Further, it imagines that there is some social or political mechanism that can produce leaders who are omniscient and capable of defining what that “common good” is.
Both datong and technocracy would require human nature to undergo a fundamental transformation. Avarice, malevolence, narcissism, psychopathy and every other deleterious failing would need to be expunged from humanity. Until they are, power will continue to be sought by those who want to control others.
The most ruthless among us will ultimately succeed—often not because they are the most suited but because they are prepared to do what others won’t in order to gain the power they crave. This situation will persist for as long as we believe that someone or some organisation needs to have absolute authority over our lives in order for us to be able to cooperate effectively.
To imagine that concentrating all power in the hands of a tiny, select band of experts or sages will solve the problems caused by the unscrupulous and frequently violent and immoral use of authority is ridiculous. You can’t fix a kakistocracy by investing more power in the “kakistocrats.”
For the global public-private partnership (G3P), which operates a compartmentalised, hierarchical, pyramid-like power structure, the most enticing aspect of technocracy is the extreme centralisation of power and authority over vast swaths of the humanity. That is why, as soon as technological development permitted and the opportunity arose, the G3P set about assisting the development of a Technate in China.
INFILTRATING CHINA
The formal story of Henry Kissinger’s “secret” 1971 discussions with Chinese Premier Chou En-lai—officially acknowledged in 2001—is that US President Richard Nixon sent Kissinger to normalise relationships with the Chinese government as a counterbalance to the Soviet Union. What is mentioned less frequently, though, is Kissinger’s relationship with the Rockefellers.
In 1956, the Rockefeller Brothers Fund commissioned Kissinger to convene its Special Studies Panels. The panels investigated emerging global challenges and trends and suggested how US foreign policy might adapt to meet them.
In the 1961 publication of the six panel reports, Prospect for America (subtitled “The problems and opportunities confronting American democracy—in foreign policy, in military preparedness, in education, in social and economic affairs”), the Rockefeller Brothers Fund outlined how public-private partnership would be key to this projected future:
Corporations, whose operations extend through many nations[,] [. . .] through which a considerable and essential part of the world’s economic activities is carried on, must be able to compose diversities, adjust conflicts of interest, and adapt their operations to the needs of the country in which they operate. In doing so they represent a further example of multinational solutions to common problems.
The authors of these reports regarded private finance as essential not only for developing international markets but also for guiding the social and political development of the target nation:
Rapid economic growth can be achieved only if local savings and public foreign investment are supplemented by an increasing inflow of private foreign investment. Such investment performs two key functions: it adds to the capital resources of the host nation and it is the chief mechanism through which the managerial and technical skills and the creative and catalytic quality can contribute to economic development in less developed areas. [. . .] Private philanthropic capital can also play an important role in economic development.
The panels that provided the analysis for Prospect for America were convened in the aftermath of McCarthyism. They needed to appeal to a US polity still obsessed with the perceived threat of international communism. Thus, the reports eulogise so-called democracy throughout.
However, there are numerous indications that the Rockefeller foreign policy strategists were willing to diplomatically suggest alternatives:
The American pattern of private enterprise and voluntary association is not the only mold for a free society.
It is clear that these strategists sought to both exploit the differences between nation-states for their development potential and amplify the importance of global issues as a means of uniting nations, regardless of their model of government, under a system of global governance. They considered scientific and technological development one way to do just that:
In the field of science, international cooperation on a world scale is most readily achievable. [. . .] [T]he United States should, therefore, seek to develop a series of agreements, looking toward the stimulation of scientific interchange and the fostering of scientific progress on a world scale. [. . .] The Communist nations should be invited to participate.
The panels, which effectively formed a temporary Rockefeller-funded think tank, were not opposed to colonialism on moral grounds but they highlighted its tactical flaws. Inherent in their critique of colonialism was an acknowledgement that alleged democratic values have nothing to do with hard-nosed geopolitics or with expansive foreign policy ambitions:
While colonialism exacted a human and political toll, it also represented one of the greatest conversions in history. As the ideals of the British, French and American revolutions became diffused, partly through the very spread of colonialism, the seeds were sown for the destruction of colonialism itself. The more successful the teachings of the colonial powers, the more untenable grew their position. Almost without exception, the leaders of independence movements fought their rulers in terms of the rulers’ own beliefs. They asked them to live up to their own principles.
The Rockefellers, being one of the leading families at the head of the G3P’s compartmentalised hierarchy, had worked with the Chinese authorities for generations. John D. Rockefeller Sr. was trading kerosene in China in 1863.
The family’s philanthropic foundation had long fostered strong ties with the Chinese government. For example, it helped advance the use of Western allopathic medicine in China by establishing the Peking Union Medical College (PUMC) and by making other philanthropic investments.
It’s safe to say that the Rockefellers were knowledgeable and enthusiastic supporters of the Chinese government. Not surprisingly, they were also knowledgeable and enthusiastic supporters of the technocracy movement in the US, maintaining their keen interest in it despite its lack of public support. They understood the potential of social engineering to create a governance of function (a Technate):
Changes in technology have always been a major cause of change in government, economic relations and social institutions. But technological innovation is no longer the work of isolated, ingenious inventors; it is the product of organised scientific enterprise and is constant, insistent and accelerating. One of its notable effects is upon the tempo of social change itself, which is enormously quicker than it has been, and which subjects every inhabitant of a technological society to its pressures. Technological innovation thus poses a series of issues with which our society will have to deal. [. . .] The growth of technological society has changed the traditional society in which men have enjoyed freedom. Large and complex organisations have become the order of the day. [. . .] Programs for the preservation and strengthening of individual freedom must assume the existence and the inevitability of such organisations.
The Rockefellers had a nuanced appreciation of the potential for technological development to act as the catalyst for change. Despite the report’s primary focus on the US relationship with the Soviet Union, the Rockefellers obviously recognised the ripe opportunities in China:
It [China] has a rapidly growing population, a shortage of resources, and a fanatical ideology. Around a large part of its perimeter exists “soft” situations, making infiltration, subversion, and outright conquest seem easy or inviting prospects. The present relations between Soviet Russia and Red China [. . .] may not always be drawn together by common interests. [. . .] We must avoid, wherever possible, courses that seem to drive China closer to the Soviets.
As founders of the Trilateral Commission, the Rockefellers’ and their fellow Trilateralists’ goal was to infiltrate China by extending the hand of cooperative friendship through public-private investment in technological and thus financial and economic development.
The Sino-Soviet split was seemingly the window of opportunity they wished to lever open.
China’s society, its political history and government structure was already amenable to the introduction of technocracy, as it was to communism. The Trilateralists were apparently eager to avoid the mistakes of Western colonialists, who extolled the democratic ideals and associated legal concepts which had come back to bite them. These ideals were, in any event, antithetical to the Trilateralists’ project.
ASSISTING CHINA
Following Mao’s death in 1976, Deng Xiaoping rose to power, becoming the Paramount Leader of the People’s Republic of China (PRC) in 1978. Just two weeks after assuming power, on January 1, 1979, he became the first communist Chinese leader to conduct a formal state visit to the US.
He was received with full state honours by the administration of Jimmy Carter, whose National Security advisor was Trilateralist Zbigniew Brzezinski—and who was himself a Trilateralist.
Deng Xiaoping immediately set about instigating a series of social and economic reforms, which were called “reform and opening up” in China and “the opening up of China” in the West.
Deng was one of a group of eight high-ranking Chinese officials who had survived the brutal repressions of cultural revolution. The reverently named “Eight Immortals” were credited with turning the Chinese economy from an unstable mess, riven with extreme poverty, into the thriving economic engine it is today.
Despite the hopes of datong, and far from being the sages that Kang Youwei dreamed of, the sons and daughters of the Eight Immortals, who are collectively known as the Princelings, hoovered up China’s state assets to effectively create a new dynasty, just as corrupt as its predecessors. Such is the nature of kakistocracy.
The scale and pace of the economic transformation in such a vast country would have been impossible without the considerable inward investment and the transfer of technology which China received from the G3P. This G3P investment was the initial source of China’s economic growth miracle. In late 2019, The World Economic Forum (WEF) reported:
High levels of government spending and foreign investment have enabled China to roughly double the size of its economy every eight years since the introduction of economic reforms in 1979.
CITIC (China International Trust & Investment Corp, renamed CITIC Group) was effectively China’s state–run investment arm. Kissinger’s visit to China had opened up investment banking opportunities for Rockefeller’s Chase Group (Chase Manhattan Bank at the time.)
In June 1980, CITIC Chairman Rong Yiren attended a meeting with David Rockefeller and the representatives of 300 Fortune 500 companies in the Chase Manhattan offices in New York.
The purpose of the meeting between CITIC and the G3P representatives was:
[To] identify and define those areas of the Chinese economy most susceptible to American technology and capital infusion.
Kissinger and Rong reportedly established an investment company, with Trilateralist Kissinger appointed as a special advisor to CITIC. The initial phase of China’s economic transformation consisted of banking reforms that allowed much greater Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in China.
FDIs aren’t just capital investments. They typically come with a transfer or sharing of expertise, technology and even workforce. Common types of FDIs are mergers, acquisitions, management services and logistical and manufacturing agreements.
From the mid 1980s onwards the G3P began to pour into Beijing’s Central Business District (CBD).
By 2009 there were 114 Western companies with a substantial presence and established investments in Beijing and beyond. By 2020 there were 238 Fortune 500 companies in Beijing. Today, Beijing CBD (called the Functional Area) now houses the regional headquarters of 105 multinational corporations and more than 4,000 foreign-invested enterprises. The CBD is one of six “high-end industrial functional areas in Beijing.”
According to Chinese state media, between 1983 and 1991 FDI in China went from a value of $920 million to $4.37 billion. By 2019 total FDI had risen to more than $2.1 trillion. At the same time, the transition economy of China, just like many other economies, rapidly expanded its money supply.
All of this monopoly money, a mixture of FDI and domestic (digital) currency printing, fuelled the economic and technological development of China. In exchange for access to its market, the Chinese government required that investors sign so-called Forced Technology Transfer (FTT) agreements.
Simultaneously, the Western mainstream media (MSM) began constantly pushing the notion of the “rising threat” of China and frequently accused China of alleged industrial espionage and “technology theft.“
Like so much propaganda aimed at Western populations by their MSM, these charges were just a fabrication. In truth, no one was forcing anyone to transfer technology to China. In fact, Trilateralists like President Bill Clinton went to considerable lengths to make sure China could get hold of the technology, including military technology, it needed.
In 1994 the Clinton administration scrapped Cold War export controls, thereby enabling more sensitive technology to be transferred to China. Claiming that they would not allow defence technology, such as supercomputer or potential uranium enrichment technology, to go to China (or Russia), they soon lifted this restriction via a work-around that shifed oversight from the departments of State and Defense to the Department of Commerce.
One only has to look at the near identical design of US and Chinese defence systems and weaponry to see that a massive amount of “sensitive” technology is common to both countries.
The asinine explanation we are given is that this is all the result of Chinese espionage, even though the US government has amended legislation to make such transfers possible.
The Israeli government and Israeli defence contractors have consistently acted as facilitators for the transfer of the most sensitive Western defence and surveillance technology to China. As soon as “reform and opening up” began in 1979, Israeli multibillionaire—then a humble billionaire—Saul Eisenberg flew a delegation of defence contractors to arrange military supply contracts with the Chinese government.
While the West’s MSM parrots the intelligence agencies’ overwhelmingly baseless claims that China represents an “immense threat,” the US government and others have maintained deep defence ties with the Israeli government for generations.
In the full and certain knowledge that Israel is passing defence technology to China, the US and other NATO allies continue to provide Israel with the latest defence technology.
Occasionally a story surfaces claiming that Washingtion is “angered” by this habitual practice. If we look beyond the propaganda, the fables simply reaffirm that which is blatantly obvious.
The Israeli government, its defence contractor and tech corporation partners, have consistently acted as a conduit for the transfer of “sensitive” defence, fintech, surveillance and communication technology from the West to China. Between 1992 and 2017 the volume of overall trade between Israel and China multiplied 200 times over.
Another Western propagandist myth is that China has “stolen” jobs from Western economies. While it is true that manufacturers took advantage of cheaper labour costs in China, leading to job losses in the West, the practice of offshoring jobs had been ongoing for decades.
Companies are in the business of maximising profits for shareholders and staying competitive. No one was forcing Western corporations to offshore. It was simply an economic expediency, largely the consequence of G3P efforts to modernise China’s economy.
Often the focus of G3P investment in China has been Research and Development (R&D). In 1994 China ranked 30th in terms of US overseas R&D investment; by 2000 it was 11th.
Between 1994 to 2001 multinational corporation (MNC) investment in China quadrupled. As a ratio of overseas R&D investment, the G3P were providing thrice the amount of “technology infusion” into China compared to anywhere else.
While the pseudopandemic sharpened the decline in total global FDI, that figure continued to rise in China.
The 4% increase of FDI in China in 2020 saw it temporarily surpass the US as the world’s leading recipient of direct investment. In 2020, while FDI in other advanced economies collapsed, China benefited from FDI valued at $163 billion.
In addition to the huge growth stimulus pumped into the Chinese economy over the last four decades, a significant number of foreign/Chinese industrial R&D alliances were established. These were separate business organizations that targeted specific research or technological development projects. They were formed through collaboration between academic and scientific research establishments, NGOs, government institutions and private enterprise.
Between 1990 and 2001 the US government established 105 such alliances. In the same time period, Japan had the second largest number of R&D partnership alliances (26), followed by Germany (15), the UK (14), Singapore (12), and Canada (11). The overwhelming majority of these R&D collaborations operated in China.
From 2001, to the financial crash in 2008, both FDI in R&D and China’s own R&D investment really took off. While the explosive pace of FDI growth slowed from 2010 onward, by 2016 China’s own outward foreign investment had surpassed the FDI it received. That was an astounding economic turnaround in less than 40 years.
A 2019 report by the World Bank stated:
China’s spending on research and development (R&D) rose to 2.18 percent of GDP in 2018, up from 1.4 percent in 2007[.] [. . .] Its spending on R&D accounts for around 20 percent of the world total, second only to the United States. Its number of patents granted annually for inventions increased from 68,000 in 2007 to 420,000 in 2017, the highest in the world. [. . .] China is also a hotbed for venture capital in search of the next technology. [. . .] China has evolved from being a net importer of FDI to a net exporter. [. . .] China remains an attractive destination for foreign investments due to its large domestic market. Foreign enterprises such as BASF, BMW, Siemens, and Tesla have recently announced new or expanded investments in China.
A focus of apparent Western concern has been China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
This enormous infrastructure project, known in China as One Belt, One Road, or OBOR, is establishing a network of modern trade routes across Eurasia, linking Asia, Africa, Europe, South East Asia and Australasia, easing both international trade and, in particular, Chinese exports.
Beyond China’s borders there are 140 countries involved in the BRI to one degree or another.
In its 2018 research paper looking at FDI in a BRI-related project, the World Bank referred to those countries directly involved in its construction as BRI nations. China’s own investment in BRI nations has grown, but the majority of its FDI goes to non-BRI nations. These, according to the World Bank, are nations that are not inviolved in the BRI.
China is the leading single nation investor in BRI nations but it does not account for the bulk of total investment. China took the lead after the 2008 financial crisis saw non-BRI nations (such as the US and the UK) pull back on their FDI deals in BRI nations. The investment from the non-BRI nations picked up again as quantitative easing (money printing) monetary policies in Western countries took effect post-2010.
The World Bank reported:
The majority of BRI countries’ [those who are part of the One Belt, One Road project] FDI inflow comes from non-BRI countries.
That is to say, BRI nations—Italy, Saudi Arabia, Austria, New Zealand, South Korea and Singapore, etc.—are net recipients of FDI from non-BRI nations, such as the US, UK, France and Germany.
The majority of the investment, expertise and technology that is building the BRI infrastructure comes from the non-BRI G3P partners. The notion that Western politicians, corporations and financial institutions are worried about the Belt and Road Initiative is just an MSM story. In reality, they are working hard to construct it in partnership with China.
CHINA: THE WORLD’S FIRST TECHNATE
China has developed an overt system dedicated to the social engineering of society.
As noted in Part 1, the definition of technocracy is:
The science of social engineering, the scientific operation of the entire social mechanism to produce and distribute goods and services to the entire population.
The focus of technocracy is to direct the population to maximise the efficiency of all “functions” of society, primarily through control of the allocation of resources.
Published in 2014, the State Council Notice for planning a Social Credit System (SCS) outlined the Chinese government’s rationale for its social credit system:
The social credit system is an important component of the Socialist market economy system and the social governance system; [. . .] its foundation is a complete network covering the credit records of all members of society and the credit infrastructure; [. . .] its reward and punishment mechanisms are incentivizing trustworthiness and restricting untrustworthiness. [. . .] The establishment of a social credit system is an important foundation for comprehensively implementing the scientific viewpoint of development. [. . .] Accelerating and advancing the establishment of the social credit system is an important precondition for promoting the optimized allocation of resources.
This is a description of pure technocracy.
Western commentators often focus upon the technological aspects of China’s social credit system. China certainly operates a dystopian surveillance society, but this complements the social credit system which, as the name suggests, is an overarching system for “implementing the scientific viewpoint of development.”
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) reported that the supposedly “terrifying system doesn’t exist” in China:
[T]he system that the central government has been slowly working on is a mix of attempts to regulate the financial credit industry, enable government agencies to share data with each other, and promote state-sanctioned moral values.
MIT and its funding partners, such as the Rockefeller Foundation, have consistently highlighted the potential merits of the social credit system (SCS).
When reading that material, we must separate the rhetoric of the engineers of the social credit system from its practical application.
Like the Great Way or technocracy or communism, the political philosophy underpinning the social credit system is presented by its advocates as progressive, humanitarian and benign. Naturally, the people who impose this system would also need to be progressive, humanitarian and benign, right?
Yet, while the social credit system is effectively a massive bureaucracy, combining the digital sharing of information with legislation and various paper-shuffling exercises, there are many aspects of it that are extremely concerning.
For one thing, it creates a public-private partnership that, by rewarding good behaviour, fosters public faith in the mechanisms of the state. For another, it punishes those who aren’t duly faithful.
The SCS removes access to “privileges” from people who have broken the law and even from those who haven’t. The concept of Joint Disciplinary Action in the SCS introduces the idea that, if found “untrustworthy,” a citizen or organisation so labelled will face broader social consequences, from having their right to fly removed to restricting their ability to book “high-class” tickets on trains to impeding their employment or business opportunities.
The SCS sets up a blacklist for those deemed to have committed “misdeeds.” Thus far it has predominantly punished those who have failed to pay court fines or those considered bad debtors.
Chinese state media have praised the courts’ partnership with tech giants like Sesame Credit—the credit-scoring system of the Alibaba Group subsidiary Ant Financial.
Chinese government data, gathered from the courts and elsewhere, has been combined with private data, gathered from social media, for the purpose of lowering the financial credit score of millions of people who have been “blacklisted.”
Public humiliation and shaming are commonly used to change the blacklisted’s behaviour. The Supreme Court maintains a database of “discredited individuals” (laolai). Tech companies like TikTok, owned by Chinese company ByteDance Ltd., publish laolai lists from the publicly available data to inform its users which companies and individuals have been “discredited.”
Technology enhances the social credit system.
To register a SIM cards and new SMART phones, Chinese users must by law use face scan technology. This biometric data then informs China’s already extensive and rapidly expanding national network of facial recognition cameras.
The surveillance grid, allowing entry to everything from bus depots to safari parks, is integrating with alleged emotion-recognition technology to assess an individual’s mood and “predict” their behaviour.
China’s internet is highly regulated via the “Measures on the Administration of Internet Information Services.” The government prohibits news bloggers from commenting on any policies or political developments without a license from the Cyberspace Adminstration of China (CAC).
Again, this system operates as a public-private partnership. There are eight licensed Internet Service Providers (ISPs) in China registered with the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT), but censorship largely occurs through the state’s partnership with fintech companies and social media platforms. The censorship is overseen by the Internet Information Office.
The Chinese have to register their personal details to use the popular social media platforms. The independent sale of SIM cards and network adapters is prohibited; the cards and adapters require similar registration upon purchase and prior to use.
The Chinese authorities can block foreign websites, restricting citizens access to information from outside China, and it is a crime for anyone to facilitate the illegal flow of prohibited information into China. The Chinese authorities have effectively created the crime of information-smuggling.
Beyond inciting crimes or advocating violence or terrorism, Article 12 of China’s Cybersecurity Law outlines the other types of information that Chinese people are not permitted to share:
[Users] must not use the Internet to engage in activities endangering national security, national honour, and national interests; they must not incite subversion of national sovereignty, overturn the socialist system, incite separatism, break national unity, [. . .] create or disseminate false information to disrupt the economic or social order, or information that infringes on the reputation, privacy, intellectual property or other lawful rights and interests of others, and other such acts.
In other words, no one is permitted to question the state in China. This doesn’t stop the people from doing so, but the associated risks are high. Political dissidents can certainly expect to be censored by the social media platforms, and prison sentences are a distinct possibility for those who speak out too vociferously.
Among the major geopolitical powers, China is leading in the development of Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC). CBDC is “programmable money” and the issuer can insert “smart contracts” to control what can be bought, where it can be used and who can use it.
Bo Li, the former Deputy Governor of the Bank of China and the current Deputy Managing Director of the International Monetary Fund (IMF), speaking at the Central Bank Digital Currencies for Financial Inclusion: Risks and Rewards symposium, clarified smart contracts further:
CBDC can allow government agencies and private sector players to program [CBDC] to create smart-contracts, to allow targetted policy functions. For example[,] welfare payments [. . .], consumptions coupons, [. . .] food stamps. By programming, CBDC money can be precisely targeted [to] what kind of [things] people can own, and what kind of use [for which] this money can be utilised. For example, [. . .] for food.
At the 2022 World Economic Forum’s Davos gathering, the president of the Chinese Alibaba Group, J. Michael Evans, announced that the global tech corporation would soon roll out its personal “carbon footprint tracker.”
He said:
We’re developing, through technology, an ability for consumers to measure their own carbon footprint [. . .] That’s where they’re travelling, how they are travelling, what are they eating, what are they consuming on the platform. [. . .] So, individual carbon footprint tracker, stay tuned! We don’t have it operational yet, but this is something we’re working on.
During the initial COVID-19 lockdowns, China’s government required all businesses and public services to install Covid status app scanners, connected to the internet.
In order to access shops, restaurants, libraries, hospitals, etc., and to move between the newly created urban “zones,” the Chinese have to use their Covid app. In conjunction with the SIM and SMART phone registration requirements, combined with the biometric facial recognition technology, the public movements of the urban Chinese can be tracked 24/7 in real time by China’s public-private partnership.
The foundations for “the scientific operation of the entire social mechanism” have already been built in China. One of the major cities conducting some of its business in CBDC is Shanghai. In Shanghai’s Pudong “smart city” district, an AI integrated monitoring system is able to access the feeds from 290,000 surveillance cameras.
The deputy director of the smart city, Sheng Denden, explained the systems value to the Chinese government:
For the government, this is a tool for more efficient administration in the city.
China is not communist. It is a technocracy. It is the world’s first Technate.
THE CHINA BLAME GAME
As we have already discussed, the idea that Western governments are “opposed” to China’s government is frankly ridiculous. This is not to suggest that there aren’t tensions, but these spring from competition not trenchant animosity. China’s government, and its tech giant partners, are as much a part of G3P as any other nation. The propaganda, from both the West and the Communist Party of China, serves as a surface narrative designed to divide and rule the global population, and to exert control over the respective domestic populations.
The Trilateralists who worked tirelessly to ensure that China was able to construct a Technate are seemingly proud of their claimed achievements. In 2001, Hedley Donovan, one of the founding members of the Trilateral Commission alongside Brzezinski and the Rockefellers, wrote:
It’s no exaggeration to describe the current regime as a technocracy. [. . .] You might say that technocratic politics is a natural fit with the Chinese political culture. [. . .] During the 1980s, technocracy as a concept was much talked about, especially in the context of so-called ‘Neo-Authoritarianism.’ [. . .] The basic beliefs and assumptions of the technocrats were laid out quite plainly: Social and economic problems were akin to engineering problems and could be understood, addressed, and eventually solved as such. [. . .] Scientism underlies the post-Mao technocracy, and it is the orthodoxy against which heresies are measured.
The self-congratulation was largely misplaced. That China’s government developed a Technate owes more to that nation’s circumstances and political and social history and belief systems than it does to the ambitions of the Trilateralists.
Technocracy is intended to be a sociopolitical system where individual rights are sacrificed to communitarianism. This is contrary to the Western liberal tradition. Technocracy represented less of a culture shock to the Chinese people. Certainly this fact was another impetus for the Trilateralists to pilot technocracy in China.
Just as we in the West generally believe in individual liberty and freedom from the state, so the Chinese people largely hold that the state should strive to rule with ren along the path to the Great Way and equality for all. In both cases, the people continue to be deceived and disappointed by the “kakistocrats,” who clearly have no intention of living up to any of those principles or expectations.
The mass and widespread Chinese demonstrations against the human cost of the government’s harsh Covid lockdown measures shows that the people are not willing to simply allow the state to do whatever it likes.
While isolated protests in China are not unusual, the scale and coordination of these protests are testament to the Chinese people’s determination to resist oppression.
The Western investment in Chinese technocracy was made with a view to developing a global system, not one restricted to China. From the surveillance network and social credit to censorship and social control using CBDC, having seen what can be achieved in China, Western governments are busy trying to impose exactly the same model of technocracy upon their own people.
The Western political class cannot help but openly admire China’s technocracy. The only difference is that China’s system is publicly discussed—although rarely acknowledged as “technocracy” by name—while the rapidly emerging technocracy in the West is denied and concealed.
The G3P is ostensibly colonising Western populations yet remains eager to avoid the errors of 19th century colonialists. The Rockefellers’ research in the late 1950s highlighted the need to first justify the necessary destruction of democratic values—something all Western governments are working hard to do.
For its part, the Chinese government has had its own reasons for allowing technocracy to flourish. Technocracy fits well with China’s domestic policy ambitions. That said, there is no reason to think that the Chinese government ever intended to “export” technocracy to other nations.
Technocracy is being installed globally. This suits China’s oligarchy, accustomed as it is to operating a Technate. The Chinese government has no reason to stand in the way of the global adoption of technocracy. It is merely aligned with the global transformation, not leading it.
China’s government is not forcing other nations to adopt technocracy. Rather, all governments are collaborating to that end.
The Chinese people are not our enemy, and China is not a foe to be fought. We, the people of the Earth, are all under attack by our own G3P governments.
Loading…