Human remains discovered at the shores of Lake Mead in May, July and August as its water levels are at historic lows are just the latest consequence of a prolonged drought gripping the United States. One of the bodies found was identified as a homicide victim who died around 40 or 50 years ago, spurring speculation that the person could have been a victim of mob crime that still was prevalent in nearby Las Vegas at that time.
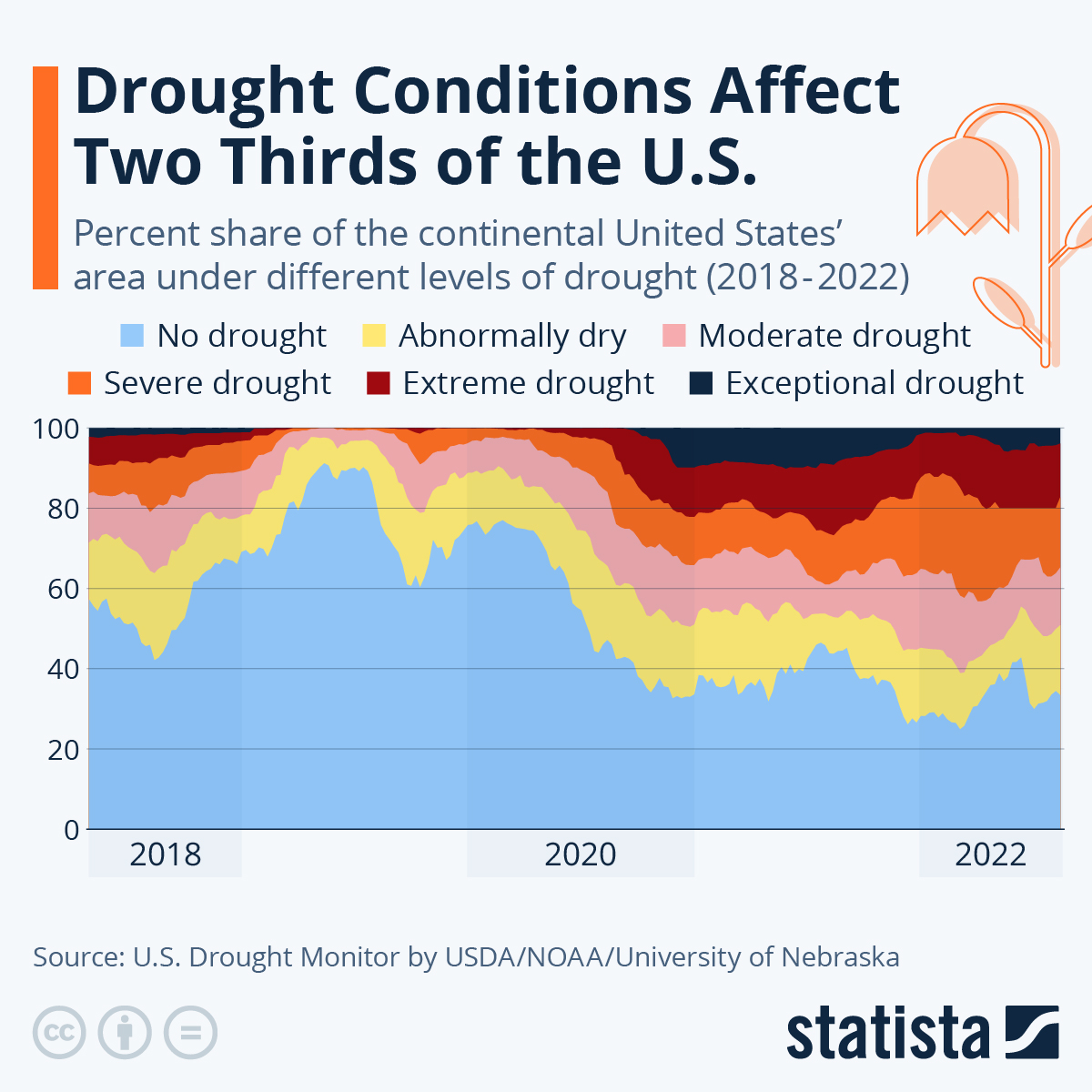
As Statista's Katharina Buchholz notes, since late 2020, the United States has been experiencing unusually hot and dry weather. According to the U.S. Drought Monitor, extreme and exceptional drought affects the American West as well as Texas most, but stretches as far as Kansas, Nebraska, Montana and Massachusetts.
The extreme circumstances have spurred demand for water and cooling, leaving reservoirs emptier than usual. With the drought also comes a heightened risk of heat-induced medical emergencies and wildfires.
As of August 16, droughts of different levels of severity affect more than 66 percent of the area of the continental United States. The number has been above the 60-percent mark since October of 2020 with just two short breaks (82 out of 98 weeks).
You will find more infographics at Statista
While it has risen this high before, it rarely stayed there for so long. During the drought of 2018, it exceeded the threshold for only five weeks. Between April 2012 and May 2013, droughts had affected more than 60 percent of the United States’ area for 60 weeks in a row and expanded to around 80 percent momentarily.
While fluctuating temperatures and very hot, very dry or very cold days are a normal phenomenon, these extreme weather events are expected to become more frequent and severe due to climate change. Scientist have connected the reoccuring drought in the Western U.S. to a changing climate, for example citing heatwaves that start earlier in the year and have become longer as well as stronger.
Human remains discovered at the shores of Lake Mead in May, July and August as its water levels are at historic lows are just the latest consequence of a prolonged drought gripping the United States. One of the bodies found was identified as a homicide victim who died around 40 or 50 years ago, spurring speculation that the person could have been a victim of mob crime that still was prevalent in nearby Las Vegas at that time.
As Statista’s Katharina Buchholz notes, since late 2020, the United States has been experiencing unusually hot and dry weather. According to the U.S. Drought Monitor, extreme and exceptional drought affects the American West as well as Texas most, but stretches as far as Kansas, Nebraska, Montana and Massachusetts.
The extreme circumstances have spurred demand for water and cooling, leaving reservoirs emptier than usual. With the drought also comes a heightened risk of heat-induced medical emergencies and wildfires.
As of August 16, droughts of different levels of severity affect more than 66 percent of the area of the continental United States. The number has been above the 60-percent mark since October of 2020 with just two short breaks (82 out of 98 weeks).
You will find more infographics at Statista
While it has risen this high before, it rarely stayed there for so long. During the drought of 2018, it exceeded the threshold for only five weeks. Between April 2012 and May 2013, droughts had affected more than 60 percent of the United States’ area for 60 weeks in a row and expanded to around 80 percent momentarily.
While fluctuating temperatures and very hot, very dry or very cold days are a normal phenomenon, these extreme weather events are expected to become more frequent and severe due to climate change. Scientist have connected the reoccuring drought in the Western U.S. to a changing climate, for example citing heatwaves that start earlier in the year and have become longer as well as stronger.