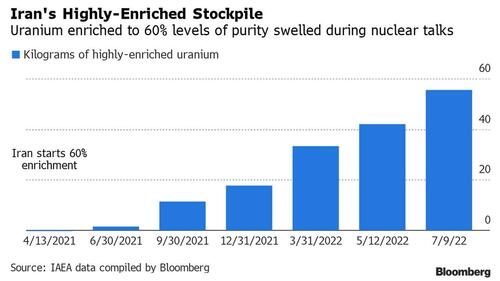
Inspectors from the UN atomic agency discovered uranium enriched to 84% purity in Iran last week, a level just below that needed for nuclear weapons, Bloomberg reported Sunday, citing two unnamed senior diplomats. Until now, Iran had been known to have enriched uranium to 60%, while a purity of 90% is needed to produce nuclear weapons.
The IAEA said in a tweet that it was “aware of recent media reports relating to uranium enrichment levels in Iran.” Director-General Rafael Grossi noted that the agency was in talks with Iran regarding the results of recent inspections, the tweet added.
The IAEA is aware of recent media reports relating to uranium enrichment levels in Iran. Director General @rafaelmgrossi states that the IAEA is discussing with Iran the results of recent Agency verification activities and will inform the IAEA Board of Governors as appropriate. pic.twitter.com/4Aqdq01Xr5
— IAEA - International Atomic Energy Agency ⚛️ (@iaeaorg) February 19, 2023
The International Atomic Energy Agency is trying to clarify how Iran accumulated the uranium enriched to 84% purity — the highest level found by inspectors in the country to date. Iran had previously told the IAEA that its centrifuges were configured to enrich uranium to a 60% level of purity. The IAEA has been preparing its quarterly Iran safeguards report ahead of a March 6 Board of Governors meeting in Vienna, where the Persian Gulf nation’s nuclear work will figure prominently on the agenda.
The report did not say where the highly enriched material was found, and comes after last month’s unannounced inspection at the Fordo nuclear site, which found two advanced centrifuges connected in a way that the Iranians had not declared to inspectors. Iran said it provided “explanations” to the inspector who reported the change and that he then “realized his mistake.”
In a joint response at the time, the United States, France, the United Kingdom, and Germany dismissed Iran’s claim as “inadequate.”

Also in January, IAEA Director-General Grossi told European Parliament lawmakers Iran had “amassed enough nuclear material for several nuclear weapons — not one at this point.” Speaking about Iran’s recent atomic activities, including enriching uranium well beyond the limits of the landmark 2015 deal to curb its nuclear capabilities — Grossi said Tehran’s trajectory “is certainly not a good one.”
The latest development comes as Iran is increasingly isolated from the West and nuclear talks with world powers remain suspended. The country has also faced widespread condemnation for its crackdown on major protests and the US and European Union have tightened sanctions on Iran over its military support for Russia’s war on Ukraine.
As Bloomberg notes, inspectors now need to determine whether Iran intentionally produced the material, or whether the concentration was an unintended accumulation within the network of pipes connecting the hundreds of fast-spinning centrifuges used to separate the isotopes. It’s the second time this month that monitors have detected suspicious enrichment-related activities.
Iran hasn’t submitted required forms declaring its intention to raise uranium enrichment levels at two facilities near the towns of Natanz and Fordow, according to one diplomat. Even if the detected material was mistakenly accumulated because of technical difficulties in operating the centrifuge cascades — something that has happened before — it underscores the danger of Iran’s decision to produce highly enriched uranium, the other diplomat said. The IAEA has said levels even at just 60% are technically indistinguishable from the level needed for a nuclear weapon. Most nuclear power reactors use material enriched to 5% purity.
The news comes just hours after earlier in Sunday, Israel blamed Iran for a Feb. 10 attack on an oil tanker in the Arabian Sea. The incident came about a fortnight after a drone strike on a weapons depot near Iran’s city of Isfahan that Tehran blamed on Israel.
Iran's deal with world powers, known as the JCPOA, collapsed after the United States withdrew from it in 2018 under then-president Donald Trump. The JCPOA gave Iran sanctions relief in return for the curbs and inspections of its nuclear facilities. After Washington withdrew, claiming the deal did not go far enough in preventing Iran from obtaining nuclear weapons, the Iranians dropped many of their own commitments to the pact and ramped up uranium enrichment. The deal had set a maximum enrichment threshold of 3.67%.
Negotiations that started in April 2021 to revive the agreement have since stalled. Iran said in November it had begun producing uranium enriched to 60% at Fordo, an underground facility that reopened three years ago after the breakdown of the JCPOA.
Inspectors from the UN atomic agency discovered uranium enriched to 84% purity in Iran last week, a level just below that needed for nuclear weapons, Bloomberg reported Sunday, citing two unnamed senior diplomats. Until now, Iran had been known to have enriched uranium to 60%, while a purity of 90% is needed to produce nuclear weapons.
The IAEA said in a tweet that it was “aware of recent media reports relating to uranium enrichment levels in Iran.” Director-General Rafael Grossi noted that the agency was in talks with Iran regarding the results of recent inspections, the tweet added.
The IAEA is aware of recent media reports relating to uranium enrichment levels in Iran. Director General @rafaelmgrossi states that the IAEA is discussing with Iran the results of recent Agency verification activities and will inform the IAEA Board of Governors as appropriate. pic.twitter.com/4Aqdq01Xr5
— IAEA – International Atomic Energy Agency ⚛️ (@iaeaorg) February 19, 2023
The International Atomic Energy Agency is trying to clarify how Iran accumulated the uranium enriched to 84% purity — the highest level found by inspectors in the country to date. Iran had previously told the IAEA that its centrifuges were configured to enrich uranium to a 60% level of purity. The IAEA has been preparing its quarterly Iran safeguards report ahead of a March 6 Board of Governors meeting in Vienna, where the Persian Gulf nation’s nuclear work will figure prominently on the agenda.
The report did not say where the highly enriched material was found, and comes after last month’s unannounced inspection at the Fordo nuclear site, which found two advanced centrifuges connected in a way that the Iranians had not declared to inspectors. Iran said it provided “explanations” to the inspector who reported the change and that he then “realized his mistake.”
In a joint response at the time, the United States, France, the United Kingdom, and Germany dismissed Iran’s claim as “inadequate.”

Also in January, IAEA Director-General Grossi told European Parliament lawmakers Iran had “amassed enough nuclear material for several nuclear weapons — not one at this point.” Speaking about Iran’s recent atomic activities, including enriching uranium well beyond the limits of the landmark 2015 deal to curb its nuclear capabilities — Grossi said Tehran’s trajectory “is certainly not a good one.”
The latest development comes as Iran is increasingly isolated from the West and nuclear talks with world powers remain suspended. The country has also faced widespread condemnation for its crackdown on major protests and the US and European Union have tightened sanctions on Iran over its military support for Russia’s war on Ukraine.
As Bloomberg notes, inspectors now need to determine whether Iran intentionally produced the material, or whether the concentration was an unintended accumulation within the network of pipes connecting the hundreds of fast-spinning centrifuges used to separate the isotopes. It’s the second time this month that monitors have detected suspicious enrichment-related activities.
Iran hasn’t submitted required forms declaring its intention to raise uranium enrichment levels at two facilities near the towns of Natanz and Fordow, according to one diplomat. Even if the detected material was mistakenly accumulated because of technical difficulties in operating the centrifuge cascades — something that has happened before — it underscores the danger of Iran’s decision to produce highly enriched uranium, the other diplomat said. The IAEA has said levels even at just 60% are technically indistinguishable from the level needed for a nuclear weapon. Most nuclear power reactors use material enriched to 5% purity.
The news comes just hours after earlier in Sunday, Israel blamed Iran for a Feb. 10 attack on an oil tanker in the Arabian Sea. The incident came about a fortnight after a drone strike on a weapons depot near Iran’s city of Isfahan that Tehran blamed on Israel.
Iran’s deal with world powers, known as the JCPOA, collapsed after the United States withdrew from it in 2018 under then-president Donald Trump. The JCPOA gave Iran sanctions relief in return for the curbs and inspections of its nuclear facilities. After Washington withdrew, claiming the deal did not go far enough in preventing Iran from obtaining nuclear weapons, the Iranians dropped many of their own commitments to the pact and ramped up uranium enrichment. The deal had set a maximum enrichment threshold of 3.67%.
Negotiations that started in April 2021 to revive the agreement have since stalled. Iran said in November it had begun producing uranium enriched to 60% at Fordo, an underground facility that reopened three years ago after the breakdown of the JCPOA.
Loading…







