Authored by Dr. Sean Lin and Mingjia Jacky Guan via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
China’s state-run medicare program recently failed to reach an agreement with Pfizer to import more Paxlovid, claiming the COVID-19 treatment drug is too expensive. This is despite the drug being offered to the state at a reduced rate in comparison with that offered to other developed countries. Lack of Paxlovid will leave only Azvudine, an anti-HIV drug the Chinese communist regime rushed through development and re-branded as an anti-COVID drug, as a treatment option.

Given the recent explosive spread of COVID and the resulting skyrocketing rates of hospitalization, finding viable treatment options is paramount.
Ivermectin in India and Peru
When the Delta variant broke out in 2021 across India, many states offered ivermectin population-wide. The efficacy of ivermectin in treating early and mild COVID-19 infections was confirmed in large states such as Uttar Pradesh—home to 241 million residents—where the use of the prophylactic dramatically reduced both the infection rate and the death toll.
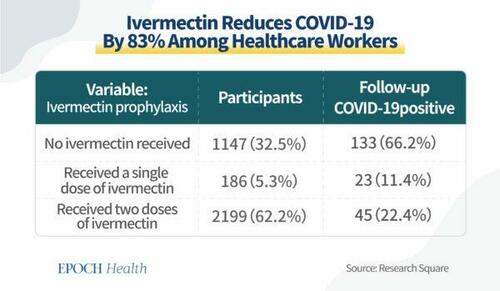
Even among frontline health care workers, ivermectin proved to be an effective prophylactic against COVID-19. One study with 3,532 frontline health care workers from the All India Institute of Medical Sciences Bhubaneswar found that two doses of oral ivermectin (300 μg/kg given 72 hours apart) as chemoprophylaxis among health care workers reduced the risk of COVID-19 infection by 83 percent in the following month.
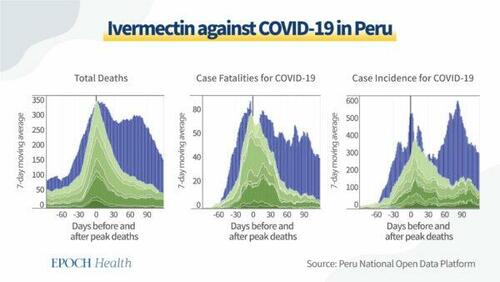
In Peru, mass ivermectin treatments were conducted through a broad-scale effort called Mega-Operación Tayta, or MOT for short. Operation MOT was led by the Peruvian army and involved 10 states, where the excess death rate saw a sharp decline with an average of 74 percent over 30 days. In 14 states where ivermectin was administered locally, the mean reduction in excess deaths over 30 days compared with deaths was 53 percent.
Lima, the capital of Peru, where the distribution of ivermectin was restricted, saw only a 25 percent reduction in excess deaths. The findings of researchers, detailed in the diagram below, show infection numbers, deaths, and fatalities across Peruvian states which implemented ivermectin (blue) and those which did not (red). The conclusion is that a reduction in deaths correlated with the distribution of ivermectin with a statistically significant p-value of less than 0.002.
Ivermectin–The Wonder Drug
Ivermectin was discovered in Japan during the late 70s as a derivative of Avermectin, produced from a single organism isolated at the Kitasato Institute in Tokyo. Since then, ivermectin has played an immeasurable role in improving the lives of billions with its humble beginnings as an anti-parasitic drug.
Ivermectin, approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and deployed worldwide since 1987, has made major inroads against two devastating tropical diseases—onchocerciasis and lymphatic filariasis. In addition, some topical forms of ivermectin are approved to treat external parasites like head lice and skin conditions such as rosacea.
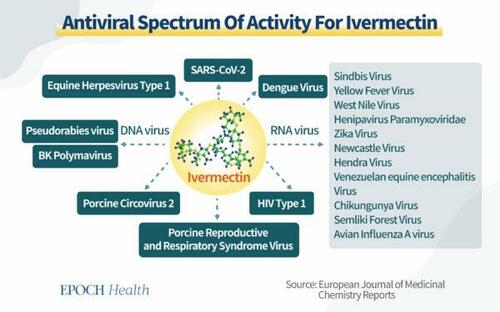
In addition to its anti-parasitic effects, a 2022 study published in the European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry Reports found that ivermectin has a strong potency at low concentrations against many DNA and RNA viruses, including HIV-1, yellow fever, malaria, West Nile virus, Zika, dengue fever, etc.
According to the study, ivermectin has an amazing inhibitory effect across multiple species and can interrupt motility and reproduction in both arthropods (such as insects) and nematodes (such as roundworms). This explains why ivermectin is prescribed for parasite infections, and also sheds light on its potential as a prophylactic against vector-borne diseases. In insects and other arthropods specifically, it can interrupt the transmission of disease.
Ivermectin’s Potential Mechanisms Against COVID
SARS-CoV-2 is a virus that takes over host cells to multiply in the body. To enter the host cells, the virus binds to the ACE-2 receptor on the surface of cells which grants them entry. Ivermectin prevents the bonding process by interfering with the virus’s spike proteins—this is the same mechanism the vaccines use.
If the virus slips past the cell membrane, its top priority is to infiltrate the brain of the cell—the DNA-containing nucleus—to start mass-producing itself. SARS-CoV-2 latches itself onto a special class of transport proteins called IMPs that have enough security clearance to enter the nucleus. In the case of a viral infection, ivermectin binds to these transport proteins and halts the interaction.
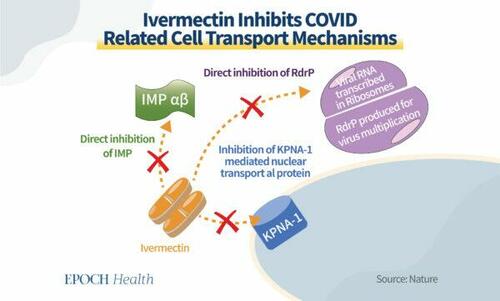
Ivermectin also inhibits the nuclear transport mechanism mediated by the KPNA-1 protein, which has a similar effect when compared with IMPs. Both proteins can enter the nucleus and ivermectin can effectively stop the virus from getting to the nucleus. In the event that the virus does manage to invade the nucleus—ivermectin also has a backup plan.
For example, when the virus has taken over and initialized self-replication, it does so through a protein called RdRp, which is at the centerpiece of viral replication—and is directly inhibited by ivermectin with very high efficacy.
Ivermectin Could Reduce Severe Lung Damage in COVID Patients
Once COVID-19 reaches later stages, it may require intensive care for recovery. For example, white lung syndrome (a hallmark symptom of acute respiratory distress syndrome) now occurring in severe COVID infections in China, is a sign that the virus has deeply infected the lungs and may have caused cytokine storms (a severe immune reaction in the body) in patients.
Other complications that arise from COVID-19 involving the lungs are conditions such as pulmonary fibrosis and hypoxia. Hypoxia occurs when the virus infects lung tissue to the extent that the alveoli, tiny sacs of air at the end of lung branches responsible for oxygen exchange, become scarred causing a severe loss of oxygen in the body.
Cytokines and chemokines are responsible for inflammation, a natural immune system response to foreign invaders. However, a large number of cytokines released into the body all at once can cause a “cytokine storm,” wherein the body is flooded with armies of white blood cells that harm the body.
A cytokine storm can be triggered through the TLR-4 pathway by the virus. The same pathway also triggers the release of nitric oxide, causing fluid leaks, dilating blood vessels, or even sepsis and fluid buildup in the lungs.
Read more here...
Authored by Dr. Sean Lin and Mingjia Jacky Guan via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
China’s state-run medicare program recently failed to reach an agreement with Pfizer to import more Paxlovid, claiming the COVID-19 treatment drug is too expensive. This is despite the drug being offered to the state at a reduced rate in comparison with that offered to other developed countries. Lack of Paxlovid will leave only Azvudine, an anti-HIV drug the Chinese communist regime rushed through development and re-branded as an anti-COVID drug, as a treatment option.

Given the recent explosive spread of COVID and the resulting skyrocketing rates of hospitalization, finding viable treatment options is paramount.
Ivermectin in India and Peru
When the Delta variant broke out in 2021 across India, many states offered ivermectin population-wide. The efficacy of ivermectin in treating early and mild COVID-19 infections was confirmed in large states such as Uttar Pradesh—home to 241 million residents—where the use of the prophylactic dramatically reduced both the infection rate and the death toll.

Even among frontline health care workers, ivermectin proved to be an effective prophylactic against COVID-19. One study with 3,532 frontline health care workers from the All India Institute of Medical Sciences Bhubaneswar found that two doses of oral ivermectin (300 μg/kg given 72 hours apart) as chemoprophylaxis among health care workers reduced the risk of COVID-19 infection by 83 percent in the following month.
In Peru, mass ivermectin treatments were conducted through a broad-scale effort called Mega-Operación Tayta, or MOT for short. Operation MOT was led by the Peruvian army and involved 10 states, where the excess death rate saw a sharp decline with an average of 74 percent over 30 days. In 14 states where ivermectin was administered locally, the mean reduction in excess deaths over 30 days compared with deaths was 53 percent.
Lima, the capital of Peru, where the distribution of ivermectin was restricted, saw only a 25 percent reduction in excess deaths. The findings of researchers, detailed in the diagram below, show infection numbers, deaths, and fatalities across Peruvian states which implemented ivermectin (blue) and those which did not (red). The conclusion is that a reduction in deaths correlated with the distribution of ivermectin with a statistically significant p-value of less than 0.002.

Ivermectin–The Wonder Drug
Ivermectin was discovered in Japan during the late 70s as a derivative of Avermectin, produced from a single organism isolated at the Kitasato Institute in Tokyo. Since then, ivermectin has played an immeasurable role in improving the lives of billions with its humble beginnings as an anti-parasitic drug.
Ivermectin, approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and deployed worldwide since 1987, has made major inroads against two devastating tropical diseases—onchocerciasis and lymphatic filariasis. In addition, some topical forms of ivermectin are approved to treat external parasites like head lice and skin conditions such as rosacea.

In addition to its anti-parasitic effects, a 2022 study published in the European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry Reports found that ivermectin has a strong potency at low concentrations against many DNA and RNA viruses, including HIV-1, yellow fever, malaria, West Nile virus, Zika, dengue fever, etc.
According to the study, ivermectin has an amazing inhibitory effect across multiple species and can interrupt motility and reproduction in both arthropods (such as insects) and nematodes (such as roundworms). This explains why ivermectin is prescribed for parasite infections, and also sheds light on its potential as a prophylactic against vector-borne diseases. In insects and other arthropods specifically, it can interrupt the transmission of disease.
Ivermectin’s Potential Mechanisms Against COVID
SARS-CoV-2 is a virus that takes over host cells to multiply in the body. To enter the host cells, the virus binds to the ACE-2 receptor on the surface of cells which grants them entry. Ivermectin prevents the bonding process by interfering with the virus’s spike proteins—this is the same mechanism the vaccines use.
If the virus slips past the cell membrane, its top priority is to infiltrate the brain of the cell—the DNA-containing nucleus—to start mass-producing itself. SARS-CoV-2 latches itself onto a special class of transport proteins called IMPs that have enough security clearance to enter the nucleus. In the case of a viral infection, ivermectin binds to these transport proteins and halts the interaction.

Ivermectin also inhibits the nuclear transport mechanism mediated by the KPNA-1 protein, which has a similar effect when compared with IMPs. Both proteins can enter the nucleus and ivermectin can effectively stop the virus from getting to the nucleus. In the event that the virus does manage to invade the nucleus—ivermectin also has a backup plan.
For example, when the virus has taken over and initialized self-replication, it does so through a protein called RdRp, which is at the centerpiece of viral replication—and is directly inhibited by ivermectin with very high efficacy.
Ivermectin Could Reduce Severe Lung Damage in COVID Patients
Once COVID-19 reaches later stages, it may require intensive care for recovery. For example, white lung syndrome (a hallmark symptom of acute respiratory distress syndrome) now occurring in severe COVID infections in China, is a sign that the virus has deeply infected the lungs and may have caused cytokine storms (a severe immune reaction in the body) in patients.
Other complications that arise from COVID-19 involving the lungs are conditions such as pulmonary fibrosis and hypoxia. Hypoxia occurs when the virus infects lung tissue to the extent that the alveoli, tiny sacs of air at the end of lung branches responsible for oxygen exchange, become scarred causing a severe loss of oxygen in the body.
Cytokines and chemokines are responsible for inflammation, a natural immune system response to foreign invaders. However, a large number of cytokines released into the body all at once can cause a “cytokine storm,” wherein the body is flooded with armies of white blood cells that harm the body.
A cytokine storm can be triggered through the TLR-4 pathway by the virus. The same pathway also triggers the release of nitric oxide, causing fluid leaks, dilating blood vessels, or even sepsis and fluid buildup in the lungs.
Read more here…
Loading…






