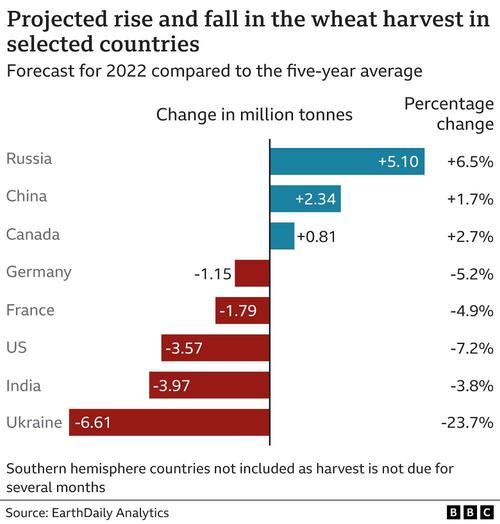
Infrared satellite imagery designed to measure moisture levels and the health of farmlands suggests that staple crops such as wheat are in poor condition and in sharp decline among major exporters including the Ukraine, the US and India. Two countries do have bumper crops so far though; namely Russia and China.
It is hard to say which governments and institutions monitor this data, but a few months ago a multitude of political leaders and global banks issued simultaneous warnings of a “global food shortage” and an impending crisis. Such institutions included the IMF, World Bank, the BIS and even the White House. So far, a perfect storm of stagflation, supply chain disruptions and poor weather conditions have combined to disrupt food production around the world.
Price inflation due to central bank stimulus measures has been enough to do incredible damage to the many national economies, but a single bad year for crops on top of this could spell disaster.
Russia and China, on the other hand, are enjoying a strategic advantage. As we entered spring of this year, the mainstream media heralded the end of the Russian economy and the swift collapse of their war efforts in Ukraine. Today, Russia is selling more oil and exporting more commodities than ever before, and both Russia and China now have the most healthy staple crops in the world. It's almost as if the public in the west has been deliberately misled about our economic strength.
Sadly, many people in the west have forgotten the importance of commodities, industry and energy in terms of geopolitical leverage. Without dominance of these three arenas there is no chance for a nation or group of nations to dictate terms to a country that has such advantages. Economic warfare is about independent production and adaptability; these are two things the US and Europe do not have right now.
With declines in crop exports, food prices will rise even further this year and there is also the possibility that Russia could cut off the EU and other nations from access to their agricultural market. Though the Kremlin says this will not happen, given the right trigger event it remains a legitimate threat. Already this month Europe is on the edge of an economic cliff as they wait to see if the Russian “maintenance shutdown” of the Nord Stream 1 pipeline is actually temporary, or the beginning of a full bore energy crisis that will last for years.
In other words, the temptation for the eastern nations to use food as a weapon against NATO countries will be just as high on their list as oil and gas. With food and energy stability in doubt there is also a considerable danger of civil unrest. Third world nations are likely to see the worst of the shortages, but price inflation in necessities is here to stay for first world countries as well. And along with that comes all the associated economic problems, including rising crime, rising unemployment and rising poverty.
Infrared satellite imagery designed to measure moisture levels and the health of farmlands suggests that staple crops such as wheat are in poor condition and in sharp decline among major exporters including the Ukraine, the US and India. Two countries do have bumper crops so far though; namely Russia and China.
It is hard to say which governments and institutions monitor this data, but a few months ago a multitude of political leaders and global banks issued simultaneous warnings of a “global food shortage” and an impending crisis. Such institutions included the IMF, World Bank, the BIS and even the White House. So far, a perfect storm of stagflation, supply chain disruptions and poor weather conditions have combined to disrupt food production around the world.
Price inflation due to central bank stimulus measures has been enough to do incredible damage to the many national economies, but a single bad year for crops on top of this could spell disaster.
Russia and China, on the other hand, are enjoying a strategic advantage. As we entered spring of this year, the mainstream media heralded the end of the Russian economy and the swift collapse of their war efforts in Ukraine. Today, Russia is selling more oil and exporting more commodities than ever before, and both Russia and China now have the most healthy staple crops in the world. It’s almost as if the public in the west has been deliberately misled about our economic strength.
Sadly, many people in the west have forgotten the importance of commodities, industry and energy in terms of geopolitical leverage. Without dominance of these three arenas there is no chance for a nation or group of nations to dictate terms to a country that has such advantages. Economic warfare is about independent production and adaptability; these are two things the US and Europe do not have right now.
With declines in crop exports, food prices will rise even further this year and there is also the possibility that Russia could cut off the EU and other nations from access to their agricultural market. Though the Kremlin says this will not happen, given the right trigger event it remains a legitimate threat. Already this month Europe is on the edge of an economic cliff as they wait to see if the Russian “maintenance shutdown” of the Nord Stream 1 pipeline is actually temporary, or the beginning of a full bore energy crisis that will last for years.
In other words, the temptation for the eastern nations to use food as a weapon against NATO countries will be just as high on their list as oil and gas. With food and energy stability in doubt there is also a considerable danger of civil unrest. Third world nations are likely to see the worst of the shortages, but price inflation in necessities is here to stay for first world countries as well. And along with that comes all the associated economic problems, including rising crime, rising unemployment and rising poverty.







