Container volumes at the twin ports of Los Angeles and Long Beach, California, are seeing steep declines versus one year ago, signaling a downturn in imported goods might suggest continued sinking economic activity.
The twin ports are the busiest container port complex in the country, responsible for 40% of all containerized flow, and are a major artery feeding overseas goods into the Heartland through rail and trucking networks.
Gene Seroka, the executive director of the Port of Los Angeles, told Bloomberg the days of more than 100 container ships waiting in queue and massive container backlogs are all but over.
Imports are sliding as major US retailers such as Walmart, Target, and Costco pull back on orders because of high inventories. Management of these retailers noted on recent earnings calls that consumer demand for big-ticket items such as electronics and furniture has waned because of elevated inflation and interest rates, leaving them with an abundance of supply in warehouses.
US retail sales tumbled in November, the Commerce Department said last month, as consumers buy staple items to survive the inflation storm rather than buying televisions and computers.
Last month, Seroka said, "We are seeing a nationwide slowing of imports."
The latest charts show West Coast transport networks are slowing.
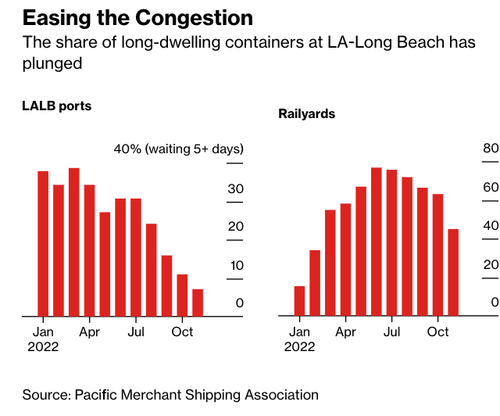
The first chart shows easing congestion at the largest containerized ports and slumping congestion on rail networks.

Seroka noted in the Bloomberg interview that easing backlogs meant processing containers through the twin ports has increased in speed.
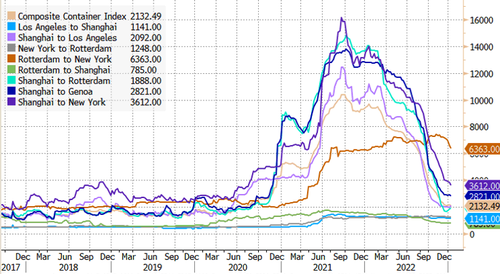
Next are container rates for major shipping lines that have plunged -- some are nearing pre-pandemic levels.
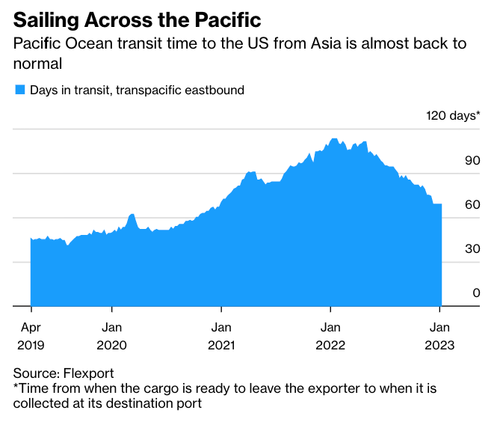
Transit times for vessels from Asia to the US are normalizing.
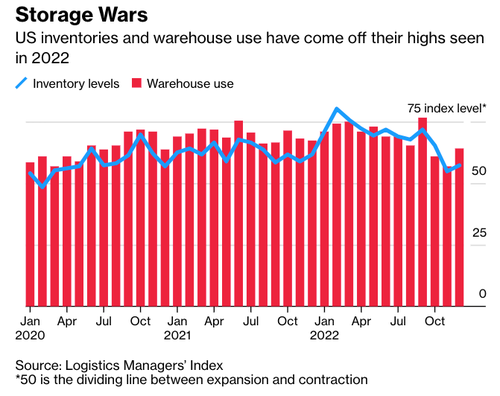
Inventory levels at warehouses are coming off a peak.
Separately, in a note on Wednesday, Goldman Sachs' Patrick Creuset told clients, "demand destruction allowed for an unwinding of supply chain bottlenecks" across the air and sea networks. He expects this "will come to an end during 1Q23, with volumes returning to modest growth through the rest of the year."
Creuset pointed out, "a record order book of containerships about to be delivered from 1Q23 through 2H24, and belly capacity set to gradually return in air cargo." The good news is that seaborne transport capacity is about to be expanded.
And according to Morgan Stanley's Ravi Shank, he expects retailers' 12-15 month de-stocking cycle could reach a bottom and begin to normalize by the midpoint of the year, and it could even lead to an upcycle in the second half.
So the good news is the shipping downturn has cleared out supply chain snarls at some of the largest US containerized ports. It seems like retailers are at an inflection point, and once de-stocking is complete, they will increase overseas orders, which might not occur until the second half.
We ask why retailers would want to increase goods on hand if the IMF and World Bank are slashing global growth estimates and warning about recession.
Container volumes at the twin ports of Los Angeles and Long Beach, California, are seeing steep declines versus one year ago, signaling a downturn in imported goods might suggest continued sinking economic activity.
The twin ports are the busiest container port complex in the country, responsible for 40% of all containerized flow, and are a major artery feeding overseas goods into the Heartland through rail and trucking networks.
Gene Seroka, the executive director of the Port of Los Angeles, told Bloomberg the days of more than 100 container ships waiting in queue and massive container backlogs are all but over.
Imports are sliding as major US retailers such as Walmart, Target, and Costco pull back on orders because of high inventories. Management of these retailers noted on recent earnings calls that consumer demand for big-ticket items such as electronics and furniture has waned because of elevated inflation and interest rates, leaving them with an abundance of supply in warehouses.
US retail sales tumbled in November, the Commerce Department said last month, as consumers buy staple items to survive the inflation storm rather than buying televisions and computers.
Last month, Seroka said, “We are seeing a nationwide slowing of imports.”
The latest charts show West Coast transport networks are slowing.
The first chart shows easing congestion at the largest containerized ports and slumping congestion on rail networks.

Seroka noted in the Bloomberg interview that easing backlogs meant processing containers through the twin ports has increased in speed.
Next are container rates for major shipping lines that have plunged — some are nearing pre-pandemic levels.
Transit times for vessels from Asia to the US are normalizing.

Inventory levels at warehouses are coming off a peak.

Separately, in a note on Wednesday, Goldman Sachs’ Patrick Creuset told clients, “demand destruction allowed for an unwinding of supply chain bottlenecks” across the air and sea networks. He expects this “will come to an end during 1Q23, with volumes returning to modest growth through the rest of the year.”
Creuset pointed out, “a record order book of containerships about to be delivered from 1Q23 through 2H24, and belly capacity set to gradually return in air cargo.” The good news is that seaborne transport capacity is about to be expanded.
And according to Morgan Stanley’s Ravi Shank, he expects retailers’ 12-15 month de-stocking cycle could reach a bottom and begin to normalize by the midpoint of the year, and it could even lead to an upcycle in the second half.
So the good news is the shipping downturn has cleared out supply chain snarls at some of the largest US containerized ports. It seems like retailers are at an inflection point, and once de-stocking is complete, they will increase overseas orders, which might not occur until the second half.
We ask why retailers would want to increase goods on hand if the IMF and World Bank are slashing global growth estimates and warning about recession.
Loading…