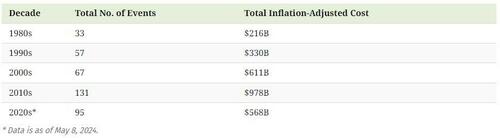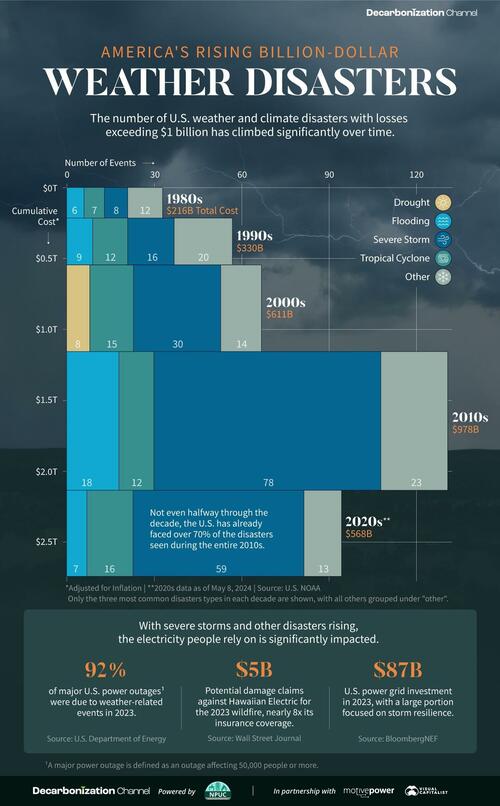
Since 1980, there have been 383 extreme weather or climate disasters where the damages reached at least $1 billion. In total, these disasters have cost more than $2.7 trillion.
Created in partnership with the National Public Utilities Council, this chart, via Visual Capitalist's Jenna Ross, shows how these disasters have been increasing with each passing decade.
A Growing Concern
The U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) tracks each disaster and estimates the cost based on factors like physical damages and time losses such as business interruption. They adjust all costs by the Consumer Price Index to account for inflation.
Both the number and cost of extreme weather disasters has grown over time. In fact, not even halfway through the 2020s the number of disasters is over 70% of those seen during the entire 2010s.
Severe storms have been the most common, accounting for half of all billion-dollar disasters since 1980. In terms of costs, tropical cyclones have caused the lion’s share—more than 50% of the total. Hurricane Katrina, which made landfall in 2005, remains the most expensive single event with $199 billion in inflation-adjusted costs.
Electricity and Extreme Weather Disasters
With severe storms and other disasters rising, the electricity people rely on is significantly impacted. For instance, droughts have been associated with a decline in hydropower, which is an important source of U.S. renewable electricity generation.
Disasters can also lead to significant costs for utility companies. Hawaii Electric faces $5 billion in potential damages claims for the 2023 wildfire, which is nearly eight times its insurance coverage. Lawsuits accuse the company of negligence in maintaining its infrastructure, such as failing to strengthen power poles to withstand high winds.
Given that the utilities industry is facing the highest risk from extreme weather and climate disasters, some companies have begun to prepare for such events. This means taking steps like burying power lines, increasing insurance coverage, and upgrading infrastructure.
Since 1980, there have been 383 extreme weather or climate disasters where the damages reached at least $1 billion. In total, these disasters have cost more than $2.7 trillion.
Created in partnership with the National Public Utilities Council, this chart, via Visual Capitalist’s Jenna Ross, shows how these disasters have been increasing with each passing decade.
A Growing Concern
The U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) tracks each disaster and estimates the cost based on factors like physical damages and time losses such as business interruption. They adjust all costs by the Consumer Price Index to account for inflation.
Both the number and cost of extreme weather disasters has grown over time. In fact, not even halfway through the 2020s the number of disasters is over 70% of those seen during the entire 2010s.
Severe storms have been the most common, accounting for half of all billion-dollar disasters since 1980. In terms of costs, tropical cyclones have caused the lion’s share—more than 50% of the total. Hurricane Katrina, which made landfall in 2005, remains the most expensive single event with $199 billion in inflation-adjusted costs.
Electricity and Extreme Weather Disasters
With severe storms and other disasters rising, the electricity people rely on is significantly impacted. For instance, droughts have been associated with a decline in hydropower, which is an important source of U.S. renewable electricity generation.
Disasters can also lead to significant costs for utility companies. Hawaii Electric faces $5 billion in potential damages claims for the 2023 wildfire, which is nearly eight times its insurance coverage. Lawsuits accuse the company of negligence in maintaining its infrastructure, such as failing to strengthen power poles to withstand high winds.
Given that the utilities industry is facing the highest risk from extreme weather and climate disasters, some companies have begun to prepare for such events. This means taking steps like burying power lines, increasing insurance coverage, and upgrading infrastructure.
Loading…