Authored by Yuhong Dong via The Epoch Times (emphasis ours),
In the series, "The HPV Vaccine: A Double-Edged Sword?" we will provide documented evidence of death and severe injuries linked with Gardasil, analyze the root cause of its harm, and offer solutions.
The Gardasil vaccine is linked to undeniable death and undeniable severe injuries as previously reported in this series of reports. An ingredient in Gardasil may contribute to these harms.
Let's shift the lens to the beautiful Pyrenees in Europe where sheep were cherished for their wool, nourishment, and companionship. However, a mysterious sheep illness occurred around a decade ago.
Mysterious Post-Vaccine Sheep Illness
In August 2006, an outbreak of bluetongue disease quickly spread to European countries causing a state of emergency.
Bluetongue disease, caused by bluetongue virus (BTV), affects ruminants, mainly sheep, with symptoms of fever, hemorrhages, depression, edemas, and generalized cyanosis, easily observed on the tongue, which explains the disease name.
The totally unexpected outbreak caused by a newly emerged BTV serotype led to a massive compulsory European vaccination campaign implemented between 2007 and 2010. The administered vaccine contained a new ingredient not used in previous BTV vaccines—aluminum (Al)—with 2.08 milligrams per milliliter as the adjuvant, in addition to inactivated BTV.

The campaign seemed to effectively halt viral spreading, however, during the same vaccination period, a series of previously unreported severe diseases emerged in France, Germany, Switzerland, the UK, and Spain, featuring weakness and various neurological symptoms. Veterinarians were stumped, as no known disease explained the tragedy.
Sheep Study Identifies the Problem
Dr. Lluis Lujan, an associate professor of veterinary pathology at the University of Zaragoza in Spain, conducted a sheep study to determine the cause of the unusual diseases.
A total of 21 sheep were assigned into three groups (red, yellow, and green) with seven in each group as follows:
- The red group received commercial sheep vaccines containing aluminum hydroxide.
- The yellow group received the equivalent dose of aluminum dissolved in water (Alhydrogel®, an aluminum-based adjuvant).
- The green group was administered a neutral saltwater solution.
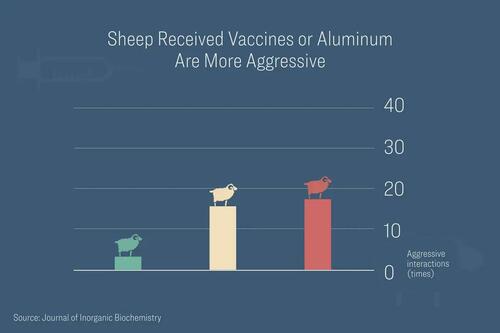
Surprisingly, both the animals from the red and yellow groups became significantly more aggressive and showed more stereotypes and higher stress.

The detected level of aluminum found in the lymph nodes in the lumbar spinal cord was much higher in both the aluminum-only (yellow) and the vaccine group (red) compared with the control group, indicating that aluminum created an extra burden needing to be processed by the sheep.
This explained the phenomenon that the sheep illness occurred only after the aluminum was added to the vaccine as an adjuvant. "So for me, yes—the reason why the animals get sick after vaccination is how the body deals with aluminum," Dr. Lujan stated in a documentary film "Under the Skin," available on Epoch TV.
The idea is not only about sheep. We are looking for something that could be happening in humans.
'Placebo' Trial Participant Had 40+ Symptoms
The Phase 3 clinical trial for Gardasil (FUTURE II study) began in 2002. A particularly large number of participants were recruited in Denmark.
Gardasil clinical trial participant, Sesilje Petersen, developed severe fatigue and a total of 40 symptoms after the second and third shots.
"It was the biggest problem because I was a student at the university and it was very difficult for me to attend the classes as I fell asleep almost daily," Sesilje said. "I wrote a list with all my symptoms—there were more than 40 symptoms, and some of them had been severe. I had a tumor on my pituitary gland."
"I received a letter and was invited to this study and it sounded very interesting. So I decided to participate," recalled Sesilje.
Sesilje kept the information brochure that the participants received at the beginning of the study. It said that the vaccination had already been carefully tested for safety and did not have any serious side effects.
The information about the placebo turned out to be a lie. "It says here that the placebo was saline—the Danish word for saltwater," she said.
Aluminum: A Toxin in Vaccines for 90 Years
Sesilje's "saline" placebo contained something highly unusual—aluminum (Al), an adjuvant commonly used in modern vaccines.
She was obviously misinformed about the study design and was unaware of what she was receiving. Prior to participating in the Gardasil study, Sesilje knew that she could not tolerate deodorants containing aluminum.
"We were not informed about the use of aluminum. The word aluminum was not given to us either in the procedure or in their phone consent form." Sesilje said.
In fact, a study by Doshi et al. found that participants in the Gardasil trials were not adequately informed that the placebo was amorphous aluminum hydroxyphosphate sulfate (AAHS). The trial participants were told they could receive a "placebo" without being informed of noninert ingredients (AAHS). This raises serious ethical concerns about the trial conduct.
Aluminum was first used in human vaccines in 1932 and was the only adjuvant used in licensed vaccines for approximately 70 years. This controversial compound is still used as an adjuvant in vaccines, however, what is its actual role?
Aluminum is the third most abundant metal in the earth’s crust and is widely present in the environment—in plants, soil, water, air, food, and pharmaceuticals. It is present in an ionic form as Al3+.
The absorption of aluminum depends on several factors such as the pH level and the presence of organic acids (citrate, lactate). It is absorbed in a proportion of only 0.1 to 0.3 percent by the gastrointestinal tract in the upper intestine.
However, when aluminum is injected into our muscles in the formulation of a vaccine, it is nearly 100 percent absorbed. It then travels and crosses the blood-brain barrier and accumulates in our brain and other organs.
Aluminum is especially harmful to our brain and nerves, as it plays multiple roles in the clumping of harmful substances (β-amyloid, tau protein) in the brain, leads to the death of brain-protective cells called astrocytes, and disrupts the "protective wall" around the brain resulting in more vulnerability to harmful substances.
Christopher Exley, an English professor of bioinorganic chemistry, is one of the most knowledgeable and widely-cited aluminum researchers in the world, with over 200 peer-reviewed scientific papers published on aluminum and over 12,000 citations.
Renal failure patients dialyzed have developed encephalitis linked to excessive brain buildup of aluminum. Those who passed away had a tenfold higher level of aluminum in gray matter, leading to fatal brain diseases in 30 to 50 percent of cases. Their brain symptoms were correlated with their blood aluminum levels, including issues of speech, coordination, cognition, and fatal seizures.
As a potent toxin, aluminum can severely harm multiple human body systems. Aluminum's toxic effects on our nerves, lungs, muscles, gut, kidneys, and liver have been well documented.
Dietary absorbed ionic aluminum can leave our body through the kidneys, however, most antigen-aluminum mixtures in vaccines are too large for the kidneys to expel out of our body. Accordingly, vaccine aluminum exposure poses a much higher safety risk than dietary aluminum.
According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), a placebo is defined as "an inactive pill, liquid, or powder that has no treatment value." The well-established toxic properties of aluminum therefore suggest that aluminum cannot constitute a valid placebo.
Toxicity Makes Aluminum an Adjuvant
Almost all modern diseases have their origin in a disturbed immune system. No other drug intervenes in the immune system as intensively as vaccines. The role of vaccine components in human immunity is discussed without taboos in the scientific community.
The gold standard to evaluate the effectiveness of a vaccine is based on the antibody level generated. In the beginning, people were not satisfied with a pure inactivated virus to provoke an immune response and wanted to find a substance to help boost immunity and generate a more robust response with longer-sustained antibodies—that is the adjuvant.
Aluminum was found to be a strong adjuvant.
According to Mr. Exley, "The known toxicity of aluminum is almost certainly a contributor to the success of aluminum-based salts as adjuvants."
A 2016 Nature study provided insight into the cellular toxicity induced by aluminum used as an adjuvant in clinically-approved human vaccinations.
When we inject a vaccine with aluminum into the muscle, we can only imagine what physical and chemical reactions will be triggered. At the very beginning, there may be little response at the injection site. The only reaction may be due to the damage caused by the needle.
"When the vaccine is injected deeply into the muscle tissue, aluminum ions begin to dissolve and start attacking the surrounding cells," Mr. Exley stated in the documentary "Under the Skin."
"So depending upon that rate of dissolution, you will get the degree of cytotoxicity—cell toxicity," he said.
The aluminum ions kill our normal healthy cells and as those cells die, they release chemical messengers, which call for help from the other immune cells.
Immune cells react immediately and start to attack anything suspicious at the vaccination site. A fierce battle takes place.
It is only in the course of this inflammation triggered by aluminum that the silent antigens are now also taken seriously and are transported away by specialized immune cells. Those silent viral proteins are also identified by immune cells as enemies and specific antibodies are produced to bind them.

Bluetongue disease, caused by bluetongue virus (BTV), affects ruminants, mainly sheep, with symptoms of fever, hemorrhages, depression, edemas, and generalized cyanosis, easily observed on the tongue, which explains the disease name.
The totally unexpected outbreak caused by a newly emerged BTV serotype led to a massive compulsory European vaccination campaign implemented between 2007 and 2010. The administered vaccine contained a new ingredient not used in previous BTV vaccines—aluminum (Al)—with 2.08 milligrams per milliliter as the adjuvant, in addition to inactivated BTV.
A total of 21 sheep were assigned into three groups (red, yellow, and green) with seven in each group as follows:
- The red group received commercial sheep vaccines containing aluminum hydroxide.
- The yellow group received the equivalent dose of aluminum dissolved in water (Alhydrogel®, an aluminum-based adjuvant).
- The green group was administered a neutral saltwater solution.
Surprisingly, both the animals from the red and yellow groups became significantly more aggressive and showed more stereotypes and higher stress.

The detected level of aluminum found in the lymph nodes in the lumbar spinal cord was much higher in both the aluminum-only (yellow) and the vaccine group (red) compared with the control group, indicating that aluminum created an extra burden needing to be processed by the sheep.
This explained the phenomenon that the sheep illness occurred only after the aluminum was added to the vaccine as an adjuvant. “So for me, yes—the reason why the animals get sick after vaccination is how the body deals with aluminum,” Dr. Lujan stated in a documentary film “Under the Skin,” available on Epoch TV.
The idea is not only about sheep. We are looking for something that could be happening in humans.
‘Placebo’ Trial Participant Had 40+ Symptoms
The Phase 3 clinical trial for Gardasil (FUTURE II study) began in 2002. A particularly large number of participants were recruited in Denmark.
Gardasil clinical trial participant, Sesilje Petersen, developed severe fatigue and a total of 40 symptoms after the second and third shots.
“It was the biggest problem because I was a student at the university and it was very difficult for me to attend the classes as I fell asleep almost daily,” Sesilje said. “I wrote a list with all my symptoms—there were more than 40 symptoms, and some of them had been severe. I had a tumor on my pituitary gland.”
“I received a letter and was invited to this study and it sounded very interesting. So I decided to participate,” recalled Sesilje.
Sesilje kept the information brochure that the participants received at the beginning of the study. It said that the vaccination had already been carefully tested for safety and did not have any serious side effects.
The information about the placebo turned out to be a lie. “It says here that the placebo was saline—the Danish word for saltwater,” she said.
Aluminum: A Toxin in Vaccines for 90 Years
Sesilje’s “saline” placebo contained something highly unusual—aluminum (Al), an adjuvant commonly used in modern vaccines.
She was obviously misinformed about the study design and was unaware of what she was receiving. Prior to participating in the Gardasil study, Sesilje knew that she could not tolerate deodorants containing aluminum.
“We were not informed about the use of aluminum. The word aluminum was not given to us either in the procedure or in their phone consent form.” Sesilje said.
In fact, a study by Doshi et al. found that participants in the Gardasil trials were not adequately informed that the placebo was amorphous aluminum hydroxyphosphate sulfate (AAHS). The trial participants were told they could receive a “placebo” without being informed of noninert ingredients (AAHS). This raises serious ethical concerns about the trial conduct.
Aluminum was first used in human vaccines in 1932 and was the only adjuvant used in licensed vaccines for approximately 70 years. This controversial compound is still used as an adjuvant in vaccines, however, what is its actual role?
Aluminum is the third most abundant metal in the earth’s crust and is widely present in the environment—in plants, soil, water, air, food, and pharmaceuticals. It is present in an ionic form as Al3+.
The absorption of aluminum depends on several factors such as the pH level and the presence of organic acids (citrate, lactate). It is absorbed in a proportion of only 0.1 to 0.3 percent by the gastrointestinal tract in the upper intestine.
However, when aluminum is injected into our muscles in the formulation of a vaccine, it is nearly 100 percent absorbed. It then travels and crosses the blood-brain barrier and accumulates in our brain and other organs.
Aluminum is especially harmful to our brain and nerves, as it plays multiple roles in the clumping of harmful substances (β-amyloid, tau protein) in the brain, leads to the death of brain-protective cells called astrocytes, and disrupts the “protective wall” around the brain resulting in more vulnerability to harmful substances.
Christopher Exley, an English professor of bioinorganic chemistry, is one of the most knowledgeable and widely-cited aluminum researchers in the world, with over 200 peer-reviewed scientific papers published on aluminum and over 12,000 citations.
Renal failure patients dialyzed have developed encephalitis linked to excessive brain buildup of aluminum. Those who passed away had a tenfold higher level of aluminum in gray matter, leading to fatal brain diseases in 30 to 50 percent of cases. Their brain symptoms were correlated with their blood aluminum levels, including issues of speech, coordination, cognition, and fatal seizures.
As a potent toxin, aluminum can severely harm multiple human body systems. Aluminum’s toxic effects on our nerves, lungs, muscles, gut, kidneys, and liver have been well documented.
Dietary absorbed ionic aluminum can leave our body through the kidneys, however, most antigen-aluminum mixtures in vaccines are too large for the kidneys to expel out of our body. Accordingly, vaccine aluminum exposure poses a much higher safety risk than dietary aluminum.
According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), a placebo is defined as “an inactive pill, liquid, or powder that has no treatment value.” The well-established toxic properties of aluminum therefore suggest that aluminum cannot constitute a valid placebo.
Toxicity Makes Aluminum an Adjuvant
Almost all modern diseases have their origin in a disturbed immune system. No other drug intervenes in the immune system as intensively as vaccines. The role of vaccine components in human immunity is discussed without taboos in the scientific community.
The gold standard to evaluate the effectiveness of a vaccine is based on the antibody level generated. In the beginning, people were not satisfied with a pure inactivated virus to provoke an immune response and wanted to find a substance to help boost immunity and generate a more robust response with longer-sustained antibodies—that is the adjuvant.
Aluminum was found to be a strong adjuvant.
According to Mr. Exley, “The known toxicity of aluminum is almost certainly a contributor to the success of aluminum-based salts as adjuvants.”
A 2016 Nature study provided insight into the cellular toxicity induced by aluminum used as an adjuvant in clinically-approved human vaccinations.
When we inject a vaccine with aluminum into the muscle, we can only imagine what physical and chemical reactions will be triggered. At the very beginning, there may be little response at the injection site. The only reaction may be due to the damage caused by the needle.
“When the vaccine is injected deeply into the muscle tissue, aluminum ions begin to dissolve and start attacking the surrounding cells,” Mr. Exley stated in the documentary “Under the Skin.”
“So depending upon that rate of dissolution, you will get the degree of cytotoxicity—cell toxicity,” he said.
The aluminum ions kill our normal healthy cells and as those cells die, they release chemical messengers, which call for help from the other immune cells.
Immune cells react immediately and start to attack anything suspicious at the vaccination site. A fierce battle takes place.
It is only in the course of this inflammation triggered by aluminum that the silent antigens are now also taken seriously and are transported away by specialized immune cells. Those silent viral proteins are also identified by immune cells as enemies and specific antibodies are produced to bind them.