Central banks around the world are getting involved in digital currencies, but some are further ahead than others.
In this map, Visual Capitalist's Marcus Ku uses data from the Atlantic Council’s Currency Tracker to visualize the state of each central banks’ digital currency effort.
Digital Currency – The Basics
Digital currencies have been around since the 1980s, but didn’t become widely popular until the launch of Bitcoin in 2009. Today, there are thousands of digital currencies in existence, also referred to as “cryptocurrencies”.
A defining feature of cryptocurrencies is that they are based on a blockchain ledger. Blockchains can be either decentralized or centralized, but the most known cryptocurrencies today (Bitcoin, Ethereum, etc.) tend to be decentralized in nature. This makes transfers and payments very difficult to trace because there is no single entity with full control.
Government-issued digital currencies, on the other hand, will be controlled by a central bank and are likely to be easily trackable. They would have the same value as the local cash currency, but instead issued digitally with no physical form.
Central Bank Digital Currencies Worldwide
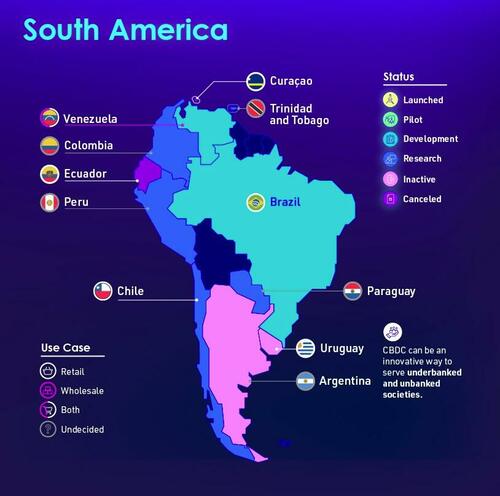
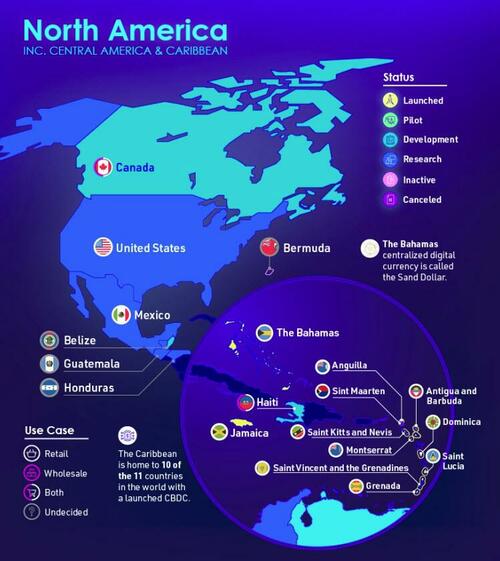
105 countries are currently exploring centralized digital currencies. Together, they represent 95% of global GDP.
When aggregated, we can see that the majority of countries are in the research stage.
We’ve also divided the map by region to make viewing easier.
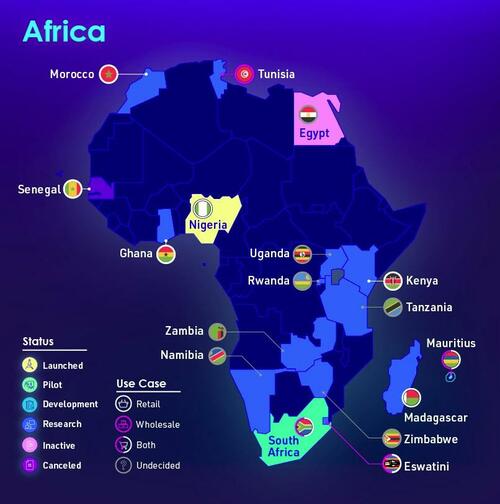
Africa
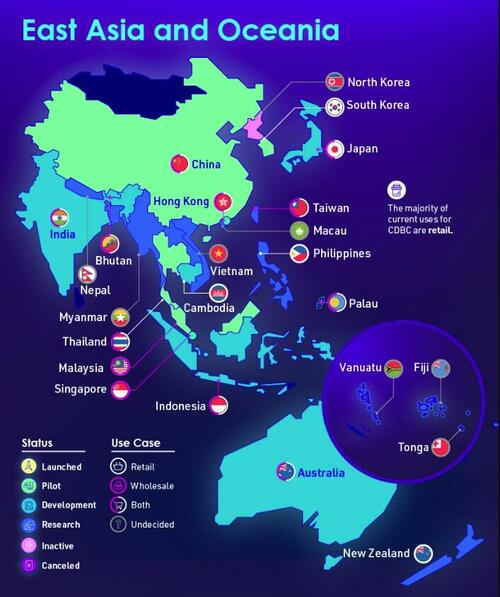
Asia
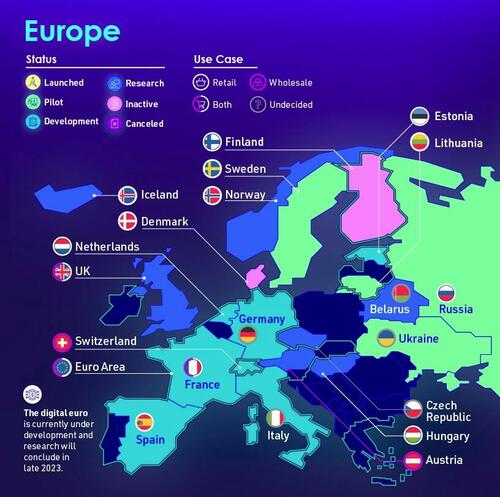
Europe
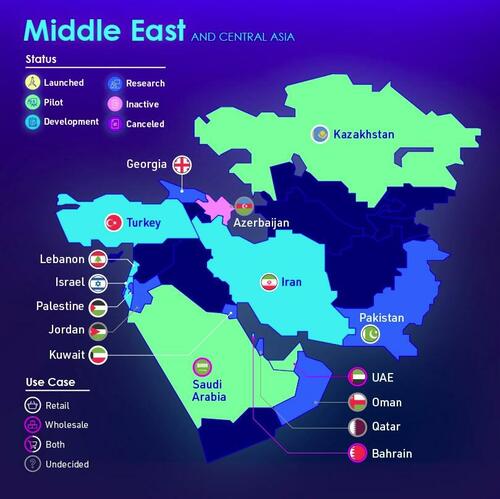
Middle East
South America
North America
What are the Benefits?
A major benefit of government-issued digital currencies is that they can improve access for underbanked people.
This is not a huge issue in developed countries like the U.S., but many people in developing nations have no access to banks and other financial services (hence the term underbanked). As the number of internet users continues to climb, digital currencies represent a sound solution.
To learn more about this topic, visit this article from Global Finance, which lists the world’s most underbanked countries in 2021.
The 9%
Just 9% of countries have launched a digital currency to date.
This includes Nigeria, which became the first African country to do so in October 2021. Half of the country’s 200 million population is believed to have no access to bank accounts.
Adoption of the eNaira (the digital version of the naira) has so far been relatively sluggish. The eNaira app has accumulated 700,000 downloads as of April 2022. That’s equal to 0.35% of the population, though not all of the downloads are users in Nigeria.
Conversely, 33.4 million Nigerians were reported to be trading or owning crypto assets, despite the Central Bank of Nigeria’s attempts to restrict usage.
Status in the U.S.
America’s central bank, the Federal Reserve, has not decided on whether it will implement a central bank digital currency (CBDC).
Our key focus is on whether and how a CBDC could improve on an already safe and efficient U.S. domestic payments system.
– FEDERAL RESERVE
To learn more, check out the Federal Reserve’s January 2022 paper on the pros and cons of CBDCs.
Central banks around the world are getting involved in digital currencies, but some are further ahead than others.
In this map, Visual Capitalist’s Marcus Ku uses data from the Atlantic Council’s Currency Tracker to visualize the state of each central banks’ digital currency effort.
Digital Currency – The Basics
Digital currencies have been around since the 1980s, but didn’t become widely popular until the launch of Bitcoin in 2009. Today, there are thousands of digital currencies in existence, also referred to as “cryptocurrencies”.
A defining feature of cryptocurrencies is that they are based on a blockchain ledger. Blockchains can be either decentralized or centralized, but the most known cryptocurrencies today (Bitcoin, Ethereum, etc.) tend to be decentralized in nature. This makes transfers and payments very difficult to trace because there is no single entity with full control.
Government-issued digital currencies, on the other hand, will be controlled by a central bank and are likely to be easily trackable. They would have the same value as the local cash currency, but instead issued digitally with no physical form.
Central Bank Digital Currencies Worldwide
105 countries are currently exploring centralized digital currencies. Together, they represent 95% of global GDP.
When aggregated, we can see that the majority of countries are in the research stage.
We’ve also divided the map by region to make viewing easier.
Africa
Asia
Europe
Middle East
South America
North America
What are the Benefits?
A major benefit of government-issued digital currencies is that they can improve access for underbanked people.
This is not a huge issue in developed countries like the U.S., but many people in developing nations have no access to banks and other financial services (hence the term underbanked). As the number of internet users continues to climb, digital currencies represent a sound solution.
To learn more about this topic, visit this article from Global Finance, which lists the world’s most underbanked countries in 2021.
The 9%
Just 9% of countries have launched a digital currency to date.
This includes Nigeria, which became the first African country to do so in October 2021. Half of the country’s 200 million population is believed to have no access to bank accounts.
Adoption of the eNaira (the digital version of the naira) has so far been relatively sluggish. The eNaira app has accumulated 700,000 downloads as of April 2022. That’s equal to 0.35% of the population, though not all of the downloads are users in Nigeria.
Conversely, 33.4 million Nigerians were reported to be trading or owning crypto assets, despite the Central Bank of Nigeria’s attempts to restrict usage.
Status in the U.S.
America’s central bank, the Federal Reserve, has not decided on whether it will implement a central bank digital currency (CBDC).
Our key focus is on whether and how a CBDC could improve on an already safe and efficient U.S. domestic payments system.
– FEDERAL RESERVE
To learn more, check out the Federal Reserve’s January 2022 paper on the pros and cons of CBDCs.