The world's largest fertilizer company warned supply disruptions could extend into 2023. A bulk of the world's supply has been taken offline due to the invasion of Ukraine by Russia. This has sparked soaring prices and shortages of crop nutrients in top growing areas worldwide; an early indication of a global food crisis could be in the beginning innings.
Bloomberg reports Canada-based Nutrien Ltd.'s CEO Ken Seitz told investors on Tuesday during a conference call that he expects to increase potash production following supply disruptions in Russia and Ukraine (both major fertilizer suppliers). Seitz expects disruptions "could last well beyond 2022."
Seitz said the conflict plus Western sanctions on Russia and Belarus has reduced fertilizer supply on global markets and could reshape crop nutrient trade, thus creating even more supply uncertainty.
"Could there be a change in global trade patterns as a result? We think that's a possibility," he said.
Fertilizer disruptions could be a multi-year event. Already, farmers worldwide are reducing fertilizers, which may threaten yields come harvest time. The repercussions could be huge: Lower yields may exacerbate the food crisis.
Here are the latest signs commercial farmers worldwide are reducing fertilizer usage because of higher prices or shortages.
Revealed last week, SLC Agricola SA, one of Brazil's largest farming operations, managing fields of soybeans, corn, and cotton fields in an area larger than the state of Delaware, will reduce the use of fertilizer by 20% and 25%.
Coffee farmers in Brazil, Nicaragua, Guatemala, and Costa Rica, some of the largest coffee-producing countries, are expected to spread less fertilizer because of high costs and shortages. A coffee cooperative representing 1,200 farmers in Costa Rica predicts coffee output could slip 15% next year because of soaring fertilizer costs.
The International Fertilizer Development Center (IFDC) warned a reduction in fertilizer use would shrink yields of rice and corn come harvest time. Farmers in China, India, Bangladesh, Indonesia, and Vietnam — the largest rice-producing countries — are spreading less fertilizer, and may result in a 10% reduction in output, equating to about 36 million tons of rice, or enough food to feed a half billion people.
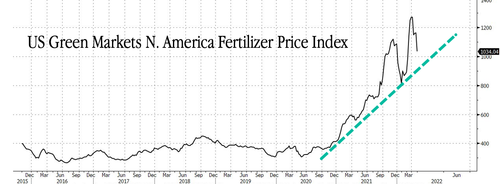
Fertilizer prices in North America have surged hundreds of percent since the summer of 2020.
"Maybe it will be a two-year problem and even then it will take two to four years after that for the deficit to catch up," The Mosaic Company's CEO Joc O'Rourke told investors during a call on Tuesday. Mosaic is a top fertilizer company in the US.
The world’s largest fertilizer company warned supply disruptions could extend into 2023. A bulk of the world’s supply has been taken offline due to the invasion of Ukraine by Russia. This has sparked soaring prices and shortages of crop nutrients in top growing areas worldwide; an early indication of a global food crisis could be in the beginning innings.
Bloomberg reports Canada-based Nutrien Ltd.’s CEO Ken Seitz told investors on Tuesday during a conference call that he expects to increase potash production following supply disruptions in Russia and Ukraine (both major fertilizer suppliers). Seitz expects disruptions “could last well beyond 2022.”
Seitz said the conflict plus Western sanctions on Russia and Belarus has reduced fertilizer supply on global markets and could reshape crop nutrient trade, thus creating even more supply uncertainty.
“Could there be a change in global trade patterns as a result? We think that’s a possibility,” he said.
Fertilizer disruptions could be a multi-year event. Already, farmers worldwide are reducing fertilizers, which may threaten yields come harvest time. The repercussions could be huge: Lower yields may exacerbate the food crisis.
Here are the latest signs commercial farmers worldwide are reducing fertilizer usage because of higher prices or shortages.
Revealed last week, SLC Agricola SA, one of Brazil’s largest farming operations, managing fields of soybeans, corn, and cotton fields in an area larger than the state of Delaware, will reduce the use of fertilizer by 20% and 25%.
Coffee farmers in Brazil, Nicaragua, Guatemala, and Costa Rica, some of the largest coffee-producing countries, are expected to spread less fertilizer because of high costs and shortages. A coffee cooperative representing 1,200 farmers in Costa Rica predicts coffee output could slip 15% next year because of soaring fertilizer costs.
The International Fertilizer Development Center (IFDC) warned a reduction in fertilizer use would shrink yields of rice and corn come harvest time. Farmers in China, India, Bangladesh, Indonesia, and Vietnam — the largest rice-producing countries — are spreading less fertilizer, and may result in a 10% reduction in output, equating to about 36 million tons of rice, or enough food to feed a half billion people.
Fertilizer prices in North America have surged hundreds of percent since the summer of 2020.
“Maybe it will be a two-year problem and even then it will take two to four years after that for the deficit to catch up,” The Mosaic Company’s CEO Joc O’Rourke told investors during a call on Tuesday. Mosaic is a top fertilizer company in the US.






