As our world has become increasingly reliant on technology and data stored online, data breaches have become an omnipresent threat to users, businesses, and government agencies; and as Visual Capitalist's Paul Sykes details below, in 2021, a new record was set with more than 5.9 billion user records stolen.
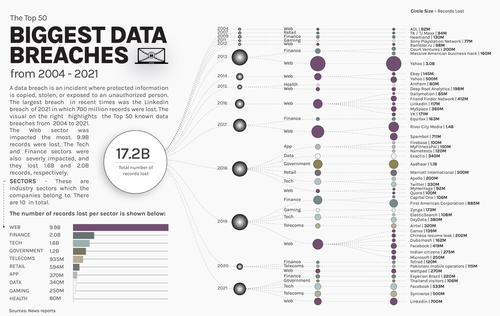
This graphic by Chimdi Nwosu visualizes the 50 largest data breaches since 2004, along with the sectors most impacted. Data was aggregated from company statements and news reports.
Understanding the Basics of Data Breaches
A data breach is an incident in which sensitive or confidential information is copied, transmitted or stolen by an unauthorized entity. This can occur as a result of malware attacks, payment card fraud, insider leaks, or unintended disclosure.
The targeted data is often customer PII (personally identifiable information), employee PII, intellectual property, corporate data or government agency data.
Date breaches can be perpetrated by lone hackers, organized cybercrime groups, or even national governments. Stolen information can then be used in other criminal enterprises such as identity theft, credit card fraud, or held for ransom payment.
Notable Data Breaches Since 2004
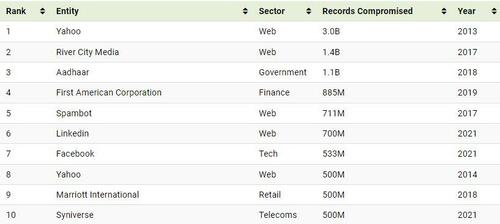
The largest data breach recorded occurred in 2013 when all three billion Yahoo accounts had their information compromised. In that cyberattack, the hackers were able to gather the personal information and passwords of users. While the full extent of the Yahoo data breach is still not fully realized, subsequent cybercrimes across the globe have been linked to the stolen information.
Here are the 10 largest data breaches by amount of user records stolen from 2004–2021.
The massive Yahoo hack accounted for roughly 30% of the 9.9 billion user records stolen from the Web sector—by far the most impacted sector. The next most-impacted sectors were Tech and Finance, with 2 billion and 1.6 billion records stolen, respectively.
Although these three sectors had the highest totals of user data lost, that doesn’t necessarily imply they have weaker security measures. Instead, it can probably be attributed to the sheer number of user records they compile.
Not all infamous data breaches are of a large scale. A smaller data breach in 2014 made headlines when Apple’s iCloud was hacked and the personal pictures of roughly 200 celebrities were disseminated across the internet. Although this highly targeted hack only affected a few hundred people, it highlighted how invasive and damaging data breaches can be to users.
The Cost of Data Breaches to Businesses
Every year data breaches cost businesses billions of dollars to prevent and contain, while also eroding consumer trust and potentially having an adverse effect on customer retention.
A 2021 IBM security report estimated that the average cost per data breach for companies in 2020 was $4.2 million, which represents a 10% increase from 2019. That increase is mainly attributed to the added security risk associated with having more people working remotely due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Measures to Improve Data Security
Completely preventing data breaches is essentially impossible, as cybercrime enterprises are often persistent, dynamic, and sophisticated. Nevertheless, businesses can seek out innovative methods to prevent exposure of data and mitigate potential damages.
For example, after the iCloud attack in 2014, Apple began avidly encouraging users to adopt two-factor authentication in an effort to strengthen data security.
Regardless of the measures businesses take, the unfortunate reality is that data breaches are a cost of doing business in the modern world and will continue to be a concern to both companies and users.
As our world has become increasingly reliant on technology and data stored online, data breaches have become an omnipresent threat to users, businesses, and government agencies; and as Visual Capitalist’s Paul Sykes details below, in 2021, a new record was set with more than 5.9 billion user records stolen.
This graphic by Chimdi Nwosu visualizes the 50 largest data breaches since 2004, along with the sectors most impacted. Data was aggregated from company statements and news reports.
Understanding the Basics of Data Breaches
A data breach is an incident in which sensitive or confidential information is copied, transmitted or stolen by an unauthorized entity. This can occur as a result of malware attacks, payment card fraud, insider leaks, or unintended disclosure.
The targeted data is often customer PII (personally identifiable information), employee PII, intellectual property, corporate data or government agency data.
Date breaches can be perpetrated by lone hackers, organized cybercrime groups, or even national governments. Stolen information can then be used in other criminal enterprises such as identity theft, credit card fraud, or held for ransom payment.
Notable Data Breaches Since 2004
The largest data breach recorded occurred in 2013 when all three billion Yahoo accounts had their information compromised. In that cyberattack, the hackers were able to gather the personal information and passwords of users. While the full extent of the Yahoo data breach is still not fully realized, subsequent cybercrimes across the globe have been linked to the stolen information.
Here are the 10 largest data breaches by amount of user records stolen from 2004–2021.
The massive Yahoo hack accounted for roughly 30% of the 9.9 billion user records stolen from the Web sector—by far the most impacted sector. The next most-impacted sectors were Tech and Finance, with 2 billion and 1.6 billion records stolen, respectively.
Although these three sectors had the highest totals of user data lost, that doesn’t necessarily imply they have weaker security measures. Instead, it can probably be attributed to the sheer number of user records they compile.
Not all infamous data breaches are of a large scale. A smaller data breach in 2014 made headlines when Apple’s iCloud was hacked and the personal pictures of roughly 200 celebrities were disseminated across the internet. Although this highly targeted hack only affected a few hundred people, it highlighted how invasive and damaging data breaches can be to users.
The Cost of Data Breaches to Businesses
Every year data breaches cost businesses billions of dollars to prevent and contain, while also eroding consumer trust and potentially having an adverse effect on customer retention.
A 2021 IBM security report estimated that the average cost per data breach for companies in 2020 was $4.2 million, which represents a 10% increase from 2019. That increase is mainly attributed to the added security risk associated with having more people working remotely due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Measures to Improve Data Security
Completely preventing data breaches is essentially impossible, as cybercrime enterprises are often persistent, dynamic, and sophisticated. Nevertheless, businesses can seek out innovative methods to prevent exposure of data and mitigate potential damages.
For example, after the iCloud attack in 2014, Apple began avidly encouraging users to adopt two-factor authentication in an effort to strengthen data security.
Regardless of the measures businesses take, the unfortunate reality is that data breaches are a cost of doing business in the modern world and will continue to be a concern to both companies and users.